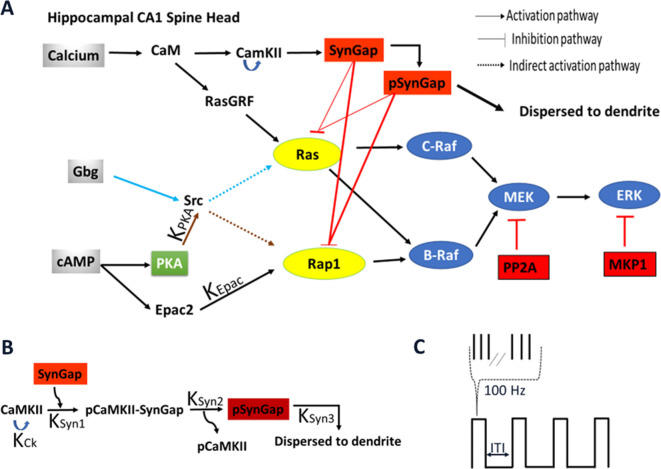
Figure 1. Schematic representation of signaling pathways activating ERK.
(A) Five pathways are included in the model: calcium activation of (1) RasGRF followed by RasGTP production or (2) CaMKII phosphorylation of SynGap followed by increasing RasGTP and Rap1GTP lifetime; cAMP activation of (3) Epac or (4) PKA phosphorylation of Src family kinase, leading to Rap1GTP production; Gi subtype of GTP binding protein (Giβγ) (5) recruits Src family kinase followed by activation of RasGTP. (B) Four effects of CaMKII on SynGap were evaluated. KCK: No autophosphorylation of CaMKII, KSyn1: No pCaMKII binding to SynGap, KSyn2: SynGap binds to pCaMKII, but cannot be phosphorylated, KSyn3: SynGap phosphorylated, but not dispersed to the dendrite. (C) LTP protocols: four trains of 100 Hz (each 1 s duration) spaced by different intertrial intervals: 3, 20, 40, 80, and 300 s.