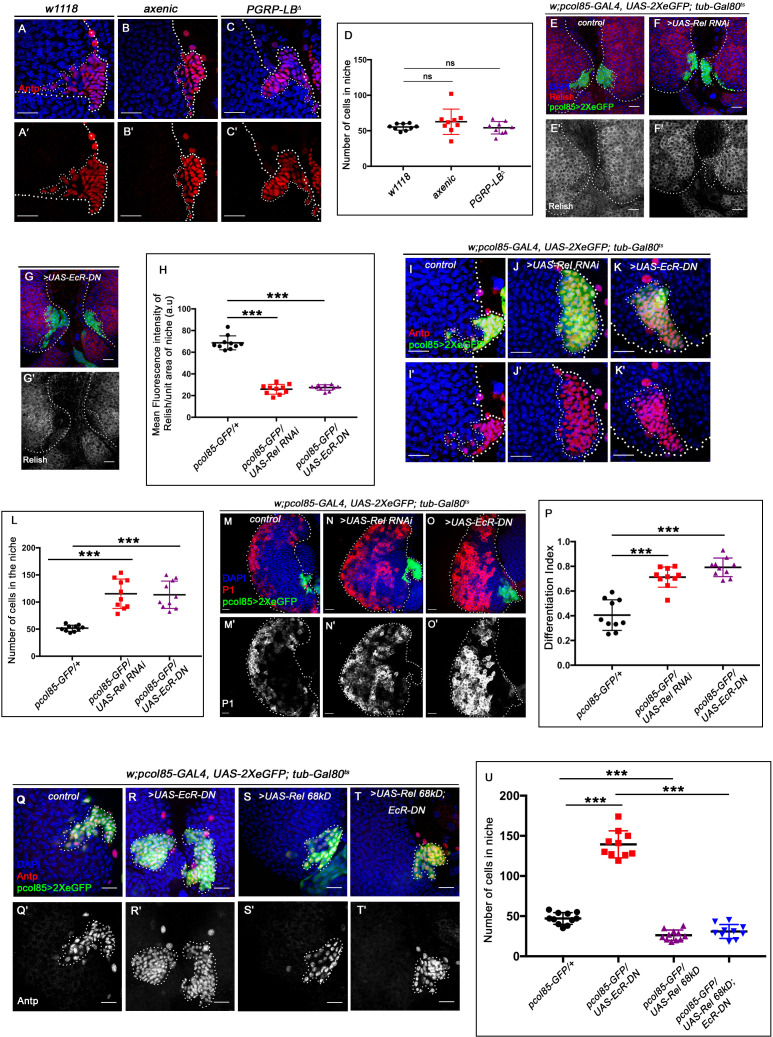
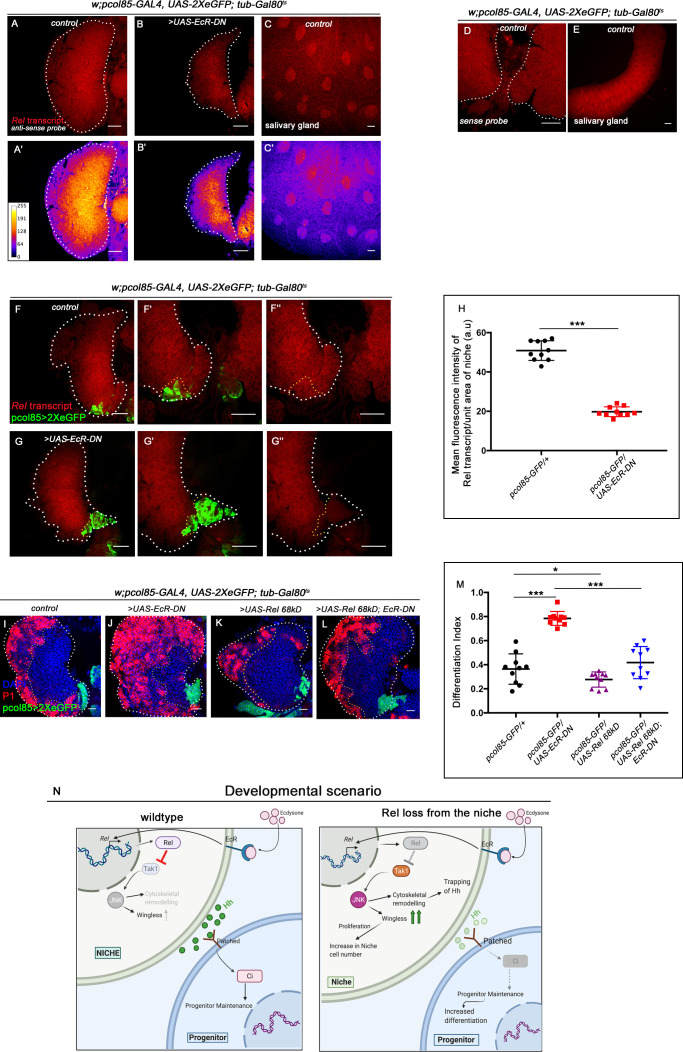
Figure 6. Ecdysone regulates Relish expression and functionality in the niche.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–C') Niche number remains comparable to control (A–A') both in axenic larval lymph gland (B–B') and in PGRP-LB mutant where there is upregulation in systemic peptidoglycan levels (C–C'). (D) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–C') (n=9; p-value = 0.262 for control versus germ free and 0.392 for control versus PGRP-LB mutant; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (E–G') Compared to that of control (E–E') Rel expression is significantly downregulated both in EcR loss (G–G') as well as in Rel loss from the niche (F–F'). (H) Statistical analysis of the data in (E–G') (n=10, p-value=7.81 × 10−12 for control versus Rel RNAi loss and p-value = 3.76 × 10−10 for control versus EcR-DN; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (I–K') Similar to Rel loss from the niche (J–J'), EcR loss also results in increase in niche cell numbers (K–K') compared to that of control (I–I'). (L) Statistical analysis of the data in I-K' (n=10, p-value=6.6 × 10−5 for control versus EcR-DN and p-value = 3.1x10−5 for control versus Rel RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (M–O') Compared to control (M–M'), both loss of Rel (N–N') and EcR (O–O') from the niche results in increase in differentiation. (P) Statistical analysis of the data in (M–O') (n=10, p-value=4.3 × 10−5 for control versus Rel RNAi and p-value=2.2 × 10−6 for control versus EcR-DN; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (Q–T') Increase in niche cell numbers observed upon EcR loss from the niche (R–R') is rescued to control levels (Q–Q') when Relish was overexpressed in an EcR loss genetic background (T–T'). Overexpression of Relish in the niche reduced the cell number compared to control (compare S–S' and Q–Q'). (U) Statistical analysis of the data in (Q–T') (n=10; p-value=1.7×10−9 for control versus EcR-DN, p-value=7.8 × 10−11 for Ecr-DN versus UAS-Rel 68kD; EcR-DN, p-value=3.63 × 10−6 for control versus UAS-Rel 68kD; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and niches in all the cases. In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.