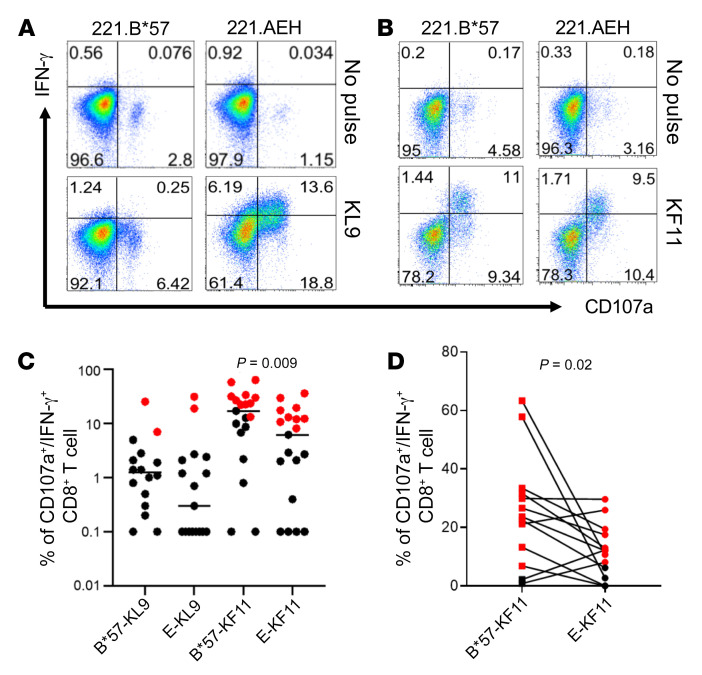
Figure 1. In vitro detection of KL9- and KF11-specific CD8+ T cell responses restricted by HLA-B*57 and HLA-E in chronically HIV-infected individuals.
Positively isolated CD8+ T cells were cultured with KL9- or KF11-pulsed (10 μg/mL) autologous adherent monocytes for 7–12 days. Polyfunctional activation was assessed after 5 hours of stimulation with target cells (221.B*57 or 221.AEH) pulsed with the peptide of interest. No peptide pulse was used as a negative control. 221.B*57 and 221.AEH are antigen-presenting 721.221 cell lines expressing single HLA-B*57:01 and HLA-E*01:01 alleles, respectively. Representative data from 2 HIV-infected individuals are shown in A and B. (A) KL9-specific reactivity restricted by B*57:01 or E*01:01 in patient CHI-7. (B) KF11-specific reactivity restricted by B*57:01 or E*01:01 in patient CHI-6. (C) Summary of KL9- and KF11-specific reactivity in HIV-infected individuals (n = 20) based on CD107a/IFN-γ expression. (D) Net frequency (CD107a/IFN-γ) of paired HLA-E and HLA-B*57 responses specific for KF11 is shown for HIV-infected individuals tested (n = 13) who mounted an HLA-E–restricted CD8+ T cell response. Black and red dots are negative and positive responses, respectively. Error bars represent median value. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test was used in C and D to determine statistical significance.