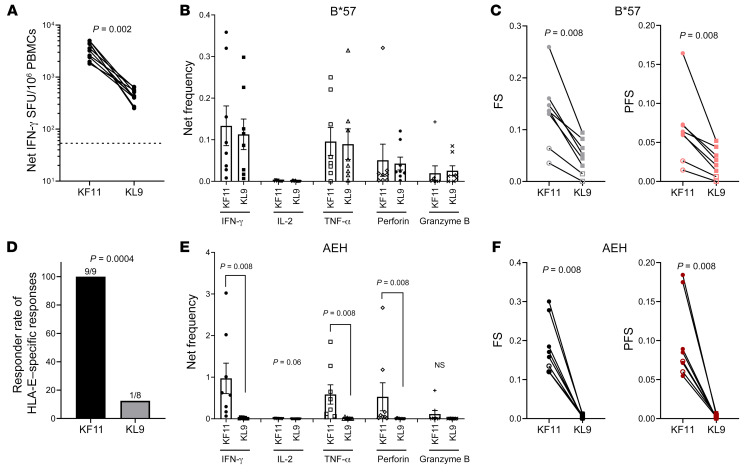
Figure 4. Ex vivo detection of KL9- and KF11-specific CD8+ T cell responses restricted by either HLA-B*57 or HLA-E in chronically HIV-infected individuals.
Positive isolated CD8+ T cells from PBMCs were cultured with target cells pulsed with 10 μg/mL peptide without long-term expansion. (A) Comparison between KF11- and KL9-induced IFN-γ response using ex vivo ELISPOT (n = 9). The dashed line represents the positive cutoff value of 55 SFU/106 PBMCs. (B and C) Net frequency of production of cytokine/effector molecules by CD8+ T cells responding to KF11/KL9 presentation by HLA-B*57 using the K562.B*57 cell line as APCs (B); and functional score (FS) and polyfunctional score (PFS) (C) (n = 8). Net frequency was calculated by subtraction of the no-peptide-pulse control of the identical APCs. (D) Comparison of responder rates between KF11-induced (n = 9) and KL9-induced (n = 8) CD8+ T cell response using HLA-E–expressing AEH cell line as APCs. (E and F) Data similar to those in B and C but for HLA-E–restricted responses: net frequency of production of cytokine/effector molecules (E); and functional score and polyfunctional score (F) (n = 8). Error bars represent mean ± SEM. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test was used in A–C, E, and F, and Fisher’s exact test in D, to determine statistical significance.