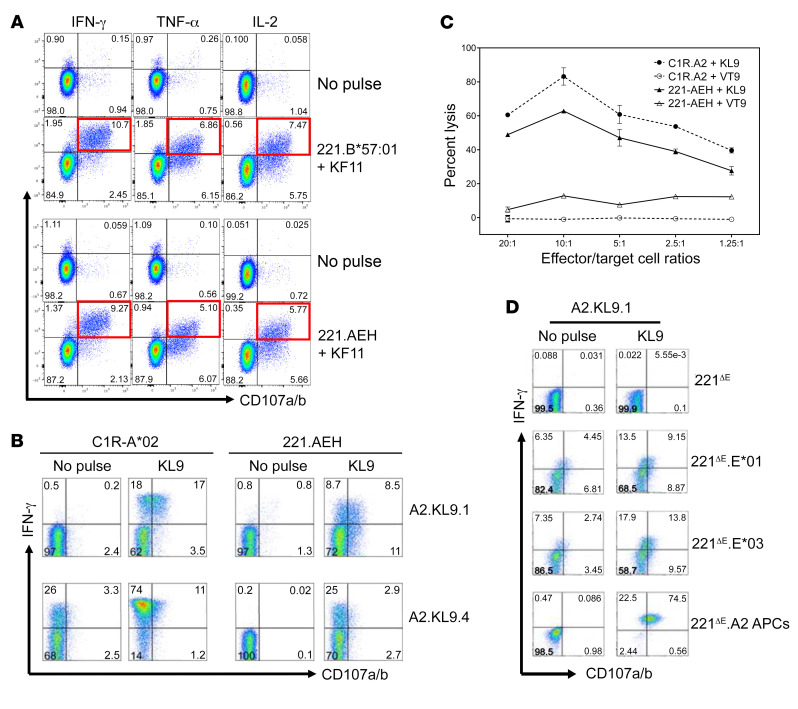
Figure 8. In vitro priming and functional characterization of HLA-E*01–restricted KF11- and KL9-specific CD8+ T cells obtained from 2 HIV-seronegative donors.
(A) KF11-specific polyfunctional responses of CD8+ T cell lines from 2 donors that are restricted by both HLA-Ia (221.B*57:01) and HLA-Ib (221.AEH) allomorphs. (B) HLA-A*02:01–restricted (C1R-A*02 used as APCs) and HLA-E–restricted (221.AEH used as APCs) KL9-specific degranulation and IFN-γ production by A*02:01-restricted KL9-specific CD8+ T cell clones (A2.KL9.1 and A2.KL9.4.) from different donors. (C) KL9-specific lysis of cognate peptide–pulsed (10 μg/mL) C1R.A2 and 221.AEH target cells by A2.KL9.1 T cells as determined by the chromium release assay. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. (D) Upregulation of surface CD107a/b expression and intracellular IFN-γ production in the A*02-restricted KL9-specific CD8+ T cells after stimulation by peptide-pulsed 221ΔE, 221ΔE.E*01, 221ΔE.E*03, or 221ΔE.A2 APCs. No response or low-level responses were observed with the no-peptide-pulse negative control.