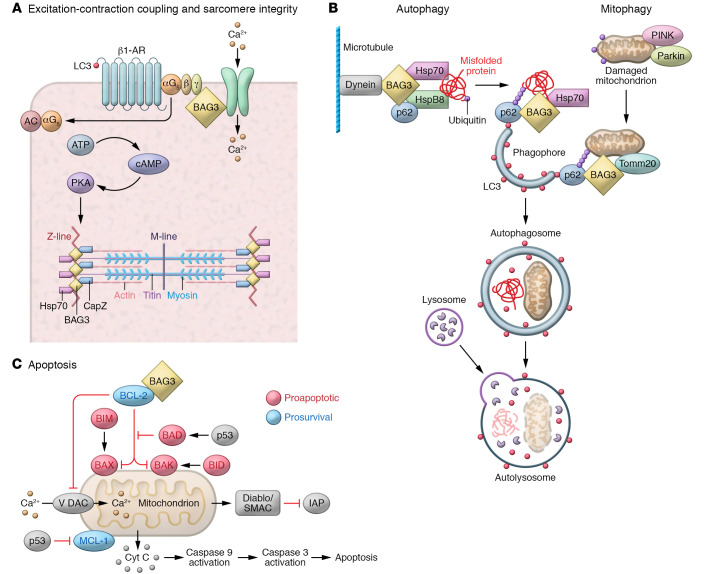
Figure 2. Diverse cellular roles of BAG3.
(A) BAG3 regulates contractility in adult ventricular myocytes, colocalizing with Na+-K+/ATPase and the L-type Ca2+ channel in the sarcolemma and the transverse tubules (t-tubules). Figure 3 shows BAG3’s function in the sarcomere in more detail. (B) BAG3 also plays a central role in autophagy and mitophagy, creating a complex including hsp70 and hspB8 to deliver ubiquitinated, misfolded proteins to the phagophore. This process is both specific and selective. BAG3 is also involved in the maturation of the phagophore into the autophagosome, through its interaction with synaptopodin-2 (SYNPO2) and its associated proteins. BAG3 also serves as an anchoring point for the dynein motor pathway, an intracellular transport system that moves cargo toward the minus ends of microtubules, where they are packaged into perinuclear aggresomes for eventual removal from the cell. (C) Finally, BAG3 couples to Bcl2 to limit the mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway.