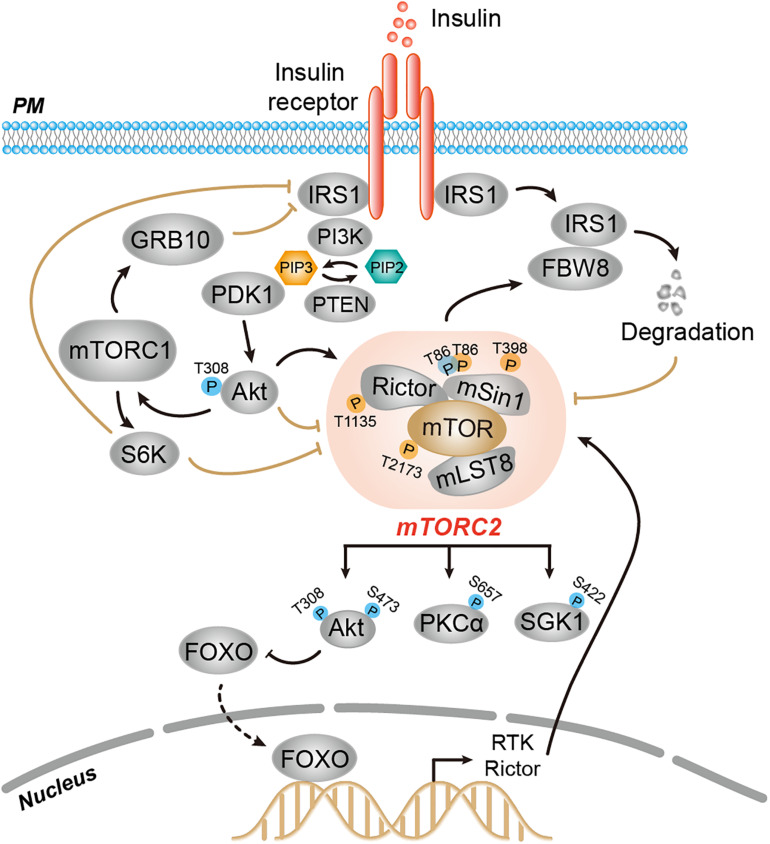
FIGURE 2.
Feedback regulation of mTORC2 activity. Several downstream signals of mTORC2, such as FBW8-IRS, mTORC1-GRB10-IRS, mTORC1-S6K-IRS, Akt, and FoxO, function as negative or positive regulators that impact mTORC2 signaling relay. Upon insulin stimulation, mTORC2 phosphorylates FBW8 to allow the translocation of FBW8 to the cytosol, which mediates ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of IRS1, thereby preventing chronic insulin signaling and mTORC2 activation. Insulin-induced mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates Grb10 to inhibit mTORC2 and Akt downstream. The mTORC1 effector S6K1 promotes phosphorylation-dependent degradation of IRS or phosphorylation of Rictor-T1135 and mSin1-T86/398 to dampen mTORC2 signaling. Akt promotes mTOR-T2173 phosphorylation to impair mTORC2 activity. Akt also positively regulates mTORC2 activity by phosphorylating mSin1-T86. Prolonged inhibition of Akt promotes FOXO-dependent transcription of RTK and Rictor.