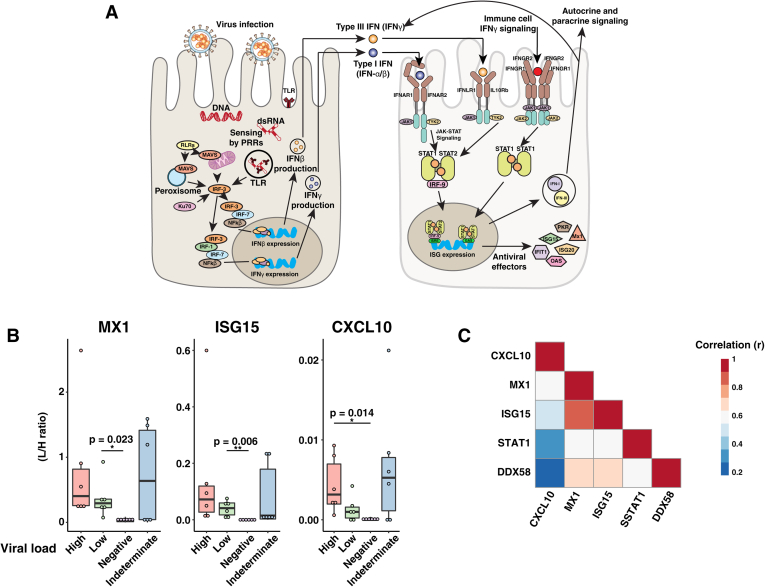
Fig. 3.
Targeted ISG measurement.A, Whisker plots displaying the stabile isotope–labeled internal standard (SIL) normalized signal for each indicated protein. B, correlation plot indicating the correlation coefficient (r) for each indicated comparison. C, interferon signaling diagram. Upon detection of viral infection, epithelial cell PRRs such as RIG-I like receptors (RLRs) and toll-like receptors (TLRs) are activated. Signaling through PRRs activates IRF family transcription factors, and together with NFκB, they induce the expression of type I and type III IFNs. IFNs act in an autocrine and paracrine manner to stimulate the expression of ISGs in uninfected neighboring cells. Epithelial cells also express type II IFN receptors (IFNGR1/2) and thus respond to IFN-γ released from immune cells. IFN, interferon; ISGs, interferon-stimulated genes; PRRs, pathogen-recognition receptors.