Figure 6.
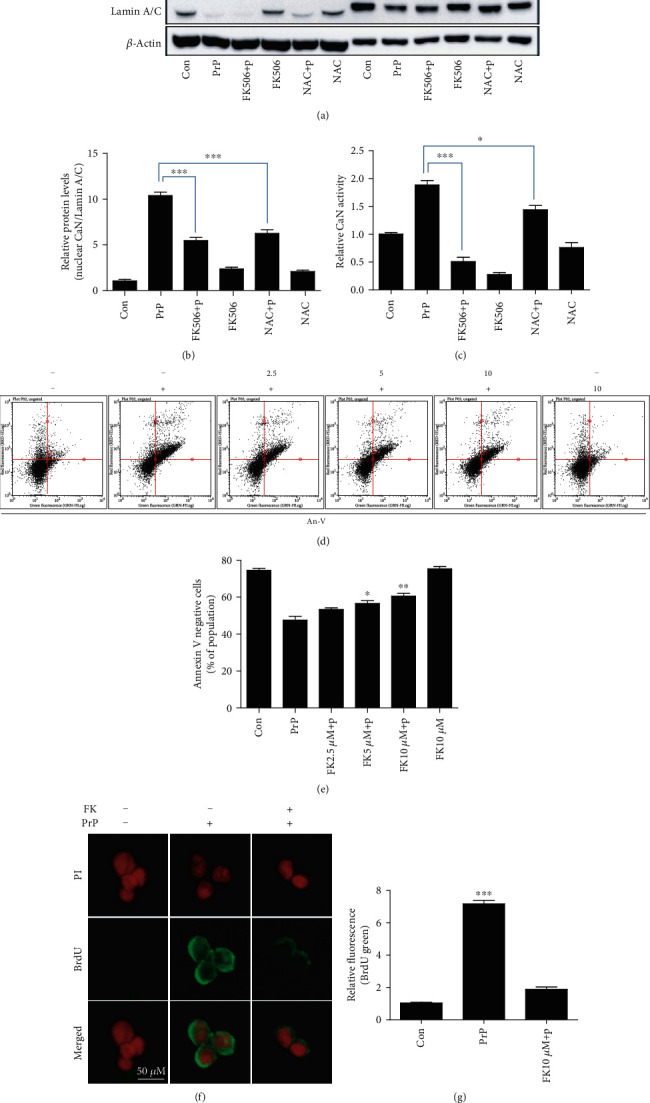
FK506 treatment attenuates PrP (106-126)-induced neurotoxicity via CaN inhibition. SK-N-SH cells were pretreated with FK506 (10 μM, 1 h) or NAC (5 mM, 1 h) and then exposed to 100 μM PrP (106-126) for 5 hours. (a) Cytosolic and nuclear fractions obtained from SK-N-SH cells induced for human calcineurin expression are analyzed by western blot with antibodies for CaN, for the cytosolic β-actin marker, and for the nuclear lamin A/C marker. (b) Bar graph representing the average nuclear CaN protein levels. The expression data were normalized to lamin A/C expression. (c) CaN activity was evaluated by a CaN activity assay. Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. PrP. (d) SK-N-SH cells were pretreated with FK506 (1 h) in a dose-dependent manner and then exposed to 100 μM PrP (106-126) for 6 hours. Cell viability was evaluated by an annexin V assay using FITC-annexin V, which combines with phosphatidylserine on the plasma membrane during apoptotic processes. (e) Bar graph showing the averages of the annexin V-negative cells. Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 10). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. PrP. (f) TUNEL-positive (green) immunofluorescence images were obtained after exposure to 100 μM PrP (106-126) (6 h) in the absence or presence of FK506 (10 μM, 1 h). The cell nuclei were counterstained with PI (red). (g) Bar graph showing the relative mean values of the green fluorescence (BrdU). Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. control.
