Figure 4.
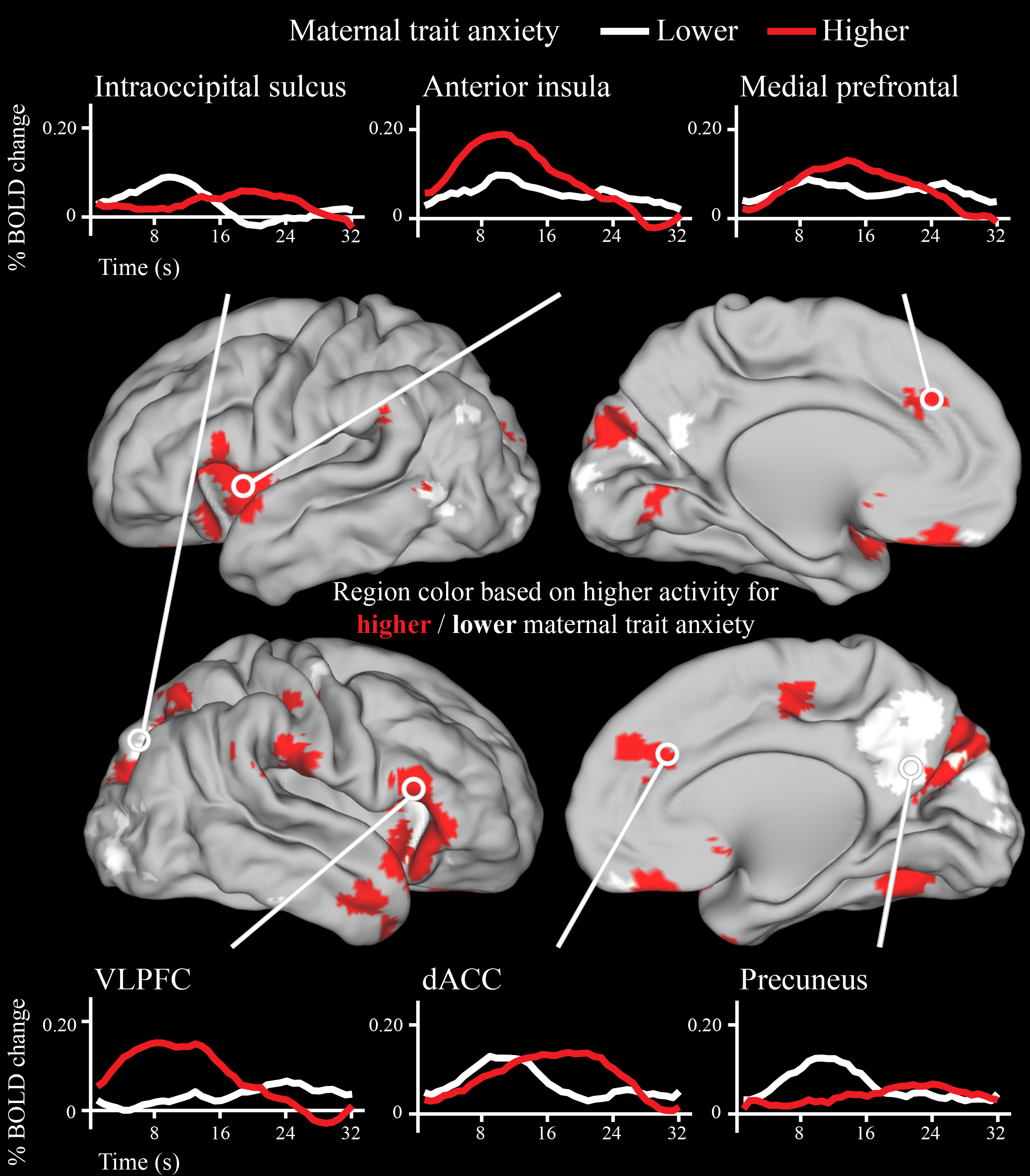
Timecourses for a subset of brain regions in which neonatal neural activity following onset of deviant sounds varied as a function of maternal trait anxiety. Note that the brain regions depicted here are identical to the brain regions in Figure 3, which is a statistical map of the same data. Trait anxiety was treated as a continuous measure in the statistical analyses, and a median split was used to generate the timecourses above solely for display purposes. Areas of cortex in red had higher peak activity in neonates born to mothers with higher trait anxiety, while areas of cortex in white had higher peak activity in neonates born to mothers with lower trait anxiety.
