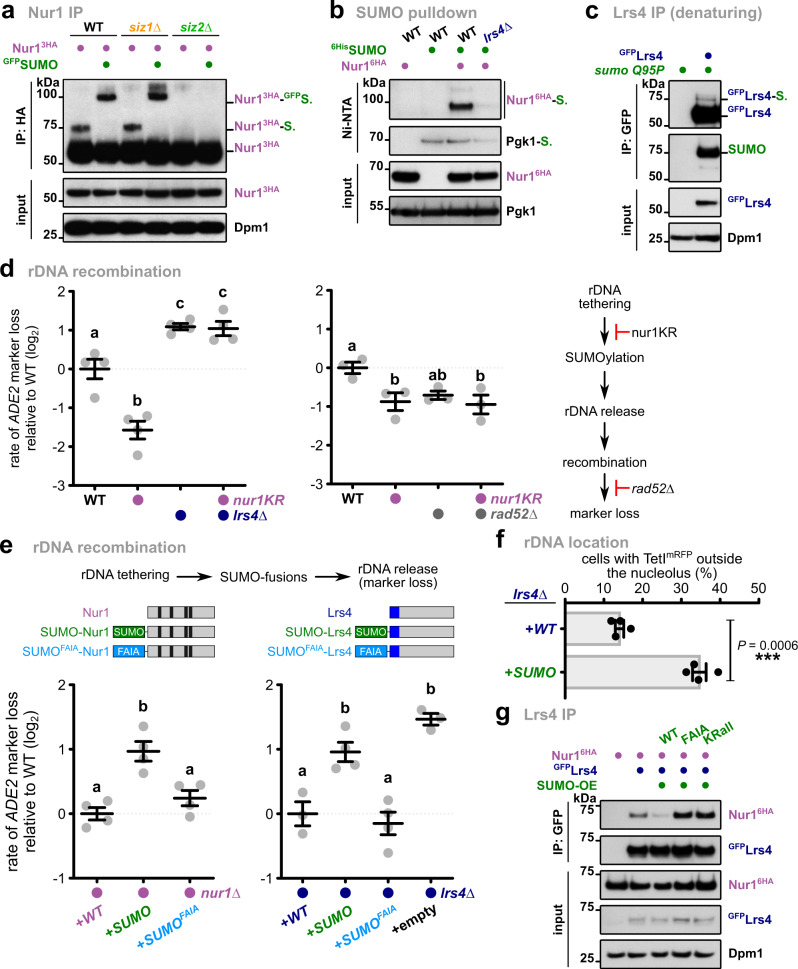
Fig. 5. SUMOylation of Nur1 and Lrs4 triggers CLIP-cohibin dissociation.
a Immunoprecipitation of Nur13HA in WT, siz1∆, and siz2∆ expressing SUMO (endogenous promoter) or GFPSUMO (ADH1 promoter). Bands corresponding to Nur1 unmodified or monoSUMOylated are labeled. Dpm1 served as loading control. b Denaturing Ni-NTA pulldowns of 6HisSUMO conjugates from WT or lrs4∆ cells expressing Nur16HA, as indicated. Pgk1 served as control for loading and pulldown efficiency. c Immunoprecipitation under semi-denaturing conditions of GFPLrs4 in cells overexpressing an isopeptidase-resistant SUMO mutant (SUMOQ95P). Detection of SUMO from immunoprecipitated samples is shown. Dpm1 served as loading control. d Rates of rDNA recombination in WT, lrs4∆ (left; n = 4) or rad52∆ (right; n = 3) cells expressing endogenously 6HA-tagged Nur1 or the SUMOylation deficient Nur1 K175-176R mutant (nur1KR). e Rates of rDNA recombination in nur1∆ or lrs4∆ cells transformed with empty vector or plasmids bearing 3HA-tagged NUR1 (left; n = 4), TAP-tagged LRS4 (right; n = 3 for LRS4 and lrs4∆; n = 4 for SUMO-LRS4 and SUMOFAIA-LRS4) or the indicated linear fusions with the endogenous promoter. Used constructs for Nur1 and Lrs4 are shown. Black, predicted transmembrane domains; blue: Csm1-interacting region. f Percentage of lrs4∆ undamaged cells transformed with plasmids bearing TAP-tagged LRS4 or SUMO-LRS4 with rDNA repeats localized outside the nucleolus, monitored as described for Fig. 2. Quantification of the marked rDNA unit was scored from four independent biological replicates, and the mean ± SEM is shown. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. g Co-immunoprecipitation of Nur16HA with GFPLrs4 in cells with endogenous SUMO levels, or strains overexpressing either SUMO WT or mutants unable to recognize SIMs (FAIA, which harbors the mutations F37A I39A) or to form SUMO chains (KRall). Dpm1 served as loading control. d, e The rate of marker loss is calculated as in Fig. 3; data are the mean ± SEM of n independent biological replicates, shown in log2 scale relative to WT. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA, and letters denote significant differences with a Tukey’s post hoc test at P ≤ 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.