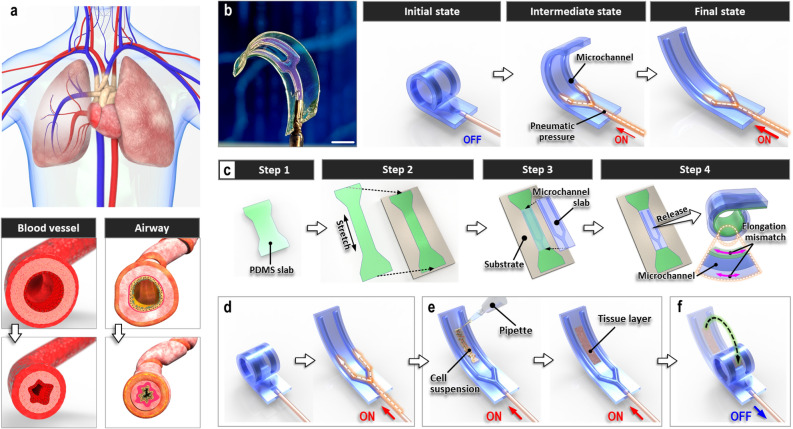
Figure 1.
A soft-robotic constrictor for dynamic compressive mechanical loading of living tissue. (a) Circumferential tissue compression occurs during the constriction of tubular organs such as blood vessels and airways. (b) Normally coiled soft robotic cell culture platform and its pneumatically driven unrolling motion. Scale bar, 5 mm. (c) Fabrication of the soft robotic device through irreversible bonding of a thin stretched PDMS strip to a microchannel-containing PDMS slab (Steps 1, 2, and 3) and subsequent release of the bonded assembly (Step 4). (d,e) Sequential steps for establishing cell culture on the microengineered device. Red arrows labeled “ON” at the bottom of schematics represent application of pneumatic pressure to the microchannels. (f) Compression of cultured tissue layer through removal of air pressure from the microchannels (shown with a blue arrow labeled “OFF”) and the resultant bending of the culture substrate.