Fig. 6. Drosophilla 5MP/Kra rescues FMRpolyG-induced neuronal toxicity.
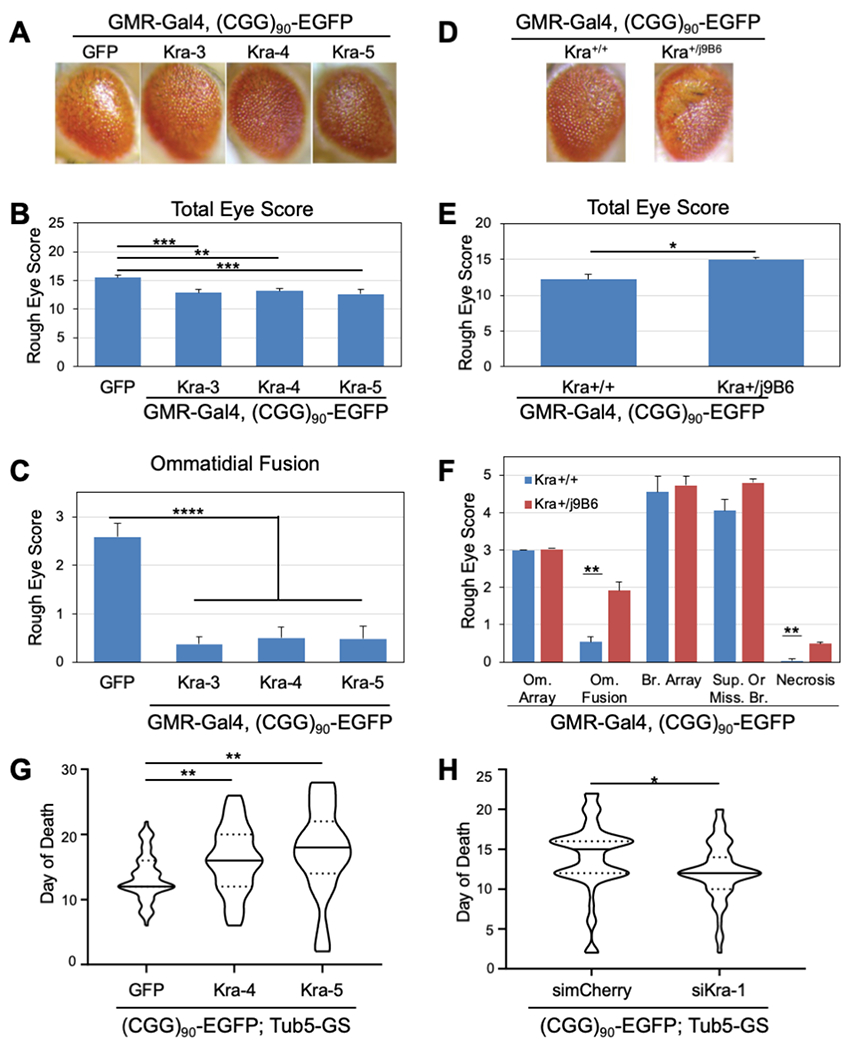
(A) Representative images of male fly eyes expressing (CGG)90-EGFP under GMR-GAL4 with Kra OE. B-C) Quantification of male B) total eye phenotype and C) ommatidial fusion phenotype of GMR-GAL4, (CGG)90-EGFP crossed to Kra OE lines. GFP serves as a control. Bars represent mean +/− stdev for 3 individual experiments (N≥25/genotype/experiment with the exception of 1 experiment for Kra-5 (N=10). One-way ANOVA B)***, C)**** with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. D) Representative images of male fly eyes expressing (CGG)90-EGFP under GMR-GAL4 with WT or heterozygous Kraj9B6 mutant. E-F) Quantification of male E) total eye phenotype and F) Individual eye category phenotype of GMR-GAL4, (CGG)90-EGFP crossed to WT or heterozygous Kraj9B6 mutant lines. Bars represent mean +/− stdev for 3 individual experiments (N≥20/genotype/experiment with the exception of 1 experiment (N≥11). Two-tailed Welch’s t-test with Bonferonni correction. G-H) Quantification of survival of flies expressing (CGG)90-EGFP under GMR-GAL4 with G) Kra OE or H) siKra. Solid lines represent median day of death, dotted lines represent 25% and 75% quartiles, for N≥35/genotype (from 2-3 experiments/genotype). Two-tailed Welch’s T-test with Bonferonni correction. *p<0.05, **p<0.01., ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.GFP and simCherry are controls.
