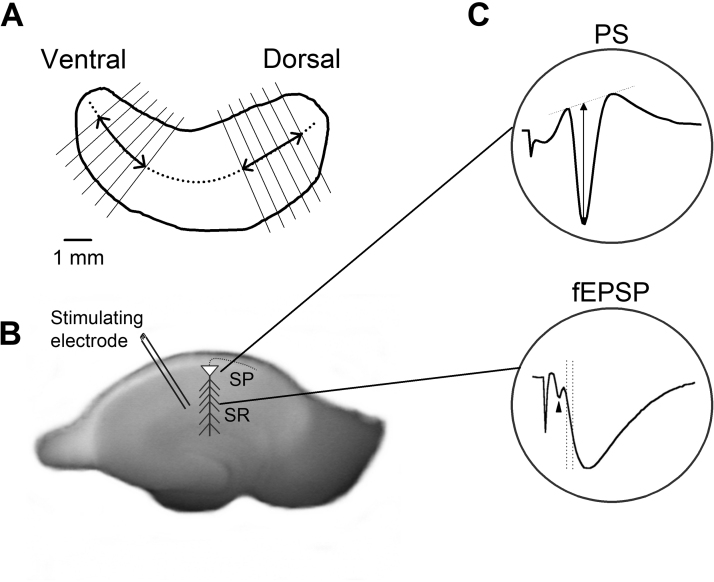
Fig. 1.
Methods used for preparing hippocampal slices and recording and quantifying field potentials. A. Drawing of a left hippocampus showing the cutting blade orientation (solid thin lines) used for preparing transverse slices (500 µm); we cut hippocampus orthogonally to its long axis (curved dotted line). Slices were prepared from the dorsal and the ventral segment of the hippocampus, extending between 1.0 and 3.5 mm from each end of the structure (solid lines with arrowheads). B. Photograph of a hippocampal slice showing the positions of stimulating and recording electrodes. Stimulating electrode was placed in CA1 stratum radiatum (SR) to activate Schaffer collaterals and recording electrodes were positioned in stratum radiatum and stratum pyramidale (SP) to record fEPSP and PS, respectively. C. The fEPSP was quantified by the maximum slope of its initial rising phase measured in a time frame of about one millisecond (denoted by the two vertical dashed lines), starting one millisecond after the peak of the presynaptic fiber volley (arrowhead). The PS was quantified by its amplitude, measured as the length of the projection of the negative peak (vertical line with arrowheads) on the line joining the two positive peaks on either side of the negative peak of the waveform (oblique dashed line).