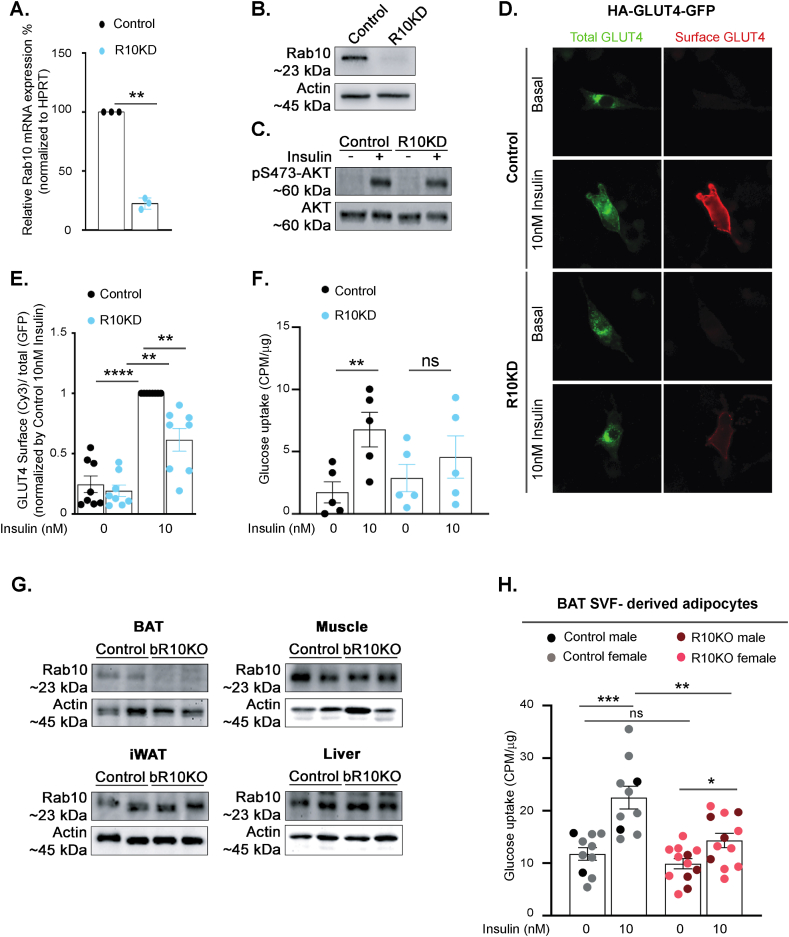
Figure 1.
Rab10 deletion impairs insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake in brown adipocytes. A. Rab10 mRNA levels in control and Rab10KD cultured murine brown adipocytes (n = 3). B. Representative Rab10 western blot of protein lysates from control and R10KD cultured brown adipocytes. C. Representative pS473-Akt and total Akt western blot of protein lysates from control and R10KD cultured brown adipocytes. D. Immunofluorescence staining of basal and 10 nM insulin-treated cultured murine brown adipocytes expressing HA-GLUT4-GFP. E. Quantification of the surface-to-total ratio of HA-GLUT4-GFP in cultured murine brown adipocytes. Each symbol is the average value from an independent experiment (n = 8 experiments). In each experiment, 15–50 cells were analyzed per condition. F. Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (CPM normalized by μg protein) in control and Rab10KD cultured murine brown adipocytes (n = 5 experiments). G. Rab10 representative immunoblots of brown adipose tissue (BAT), inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT), muscle and liver extracts from control and bR10KO mice. H. Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (CPM normalized by μg protein) in BAT SVF-derived adipocytes (n = 10–12 mice/group). Data from females are shown in grey and light red dots and data from males are shown in black and dark red dots. Student's t-test was used for comparing groups. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.