FIGURE 3.
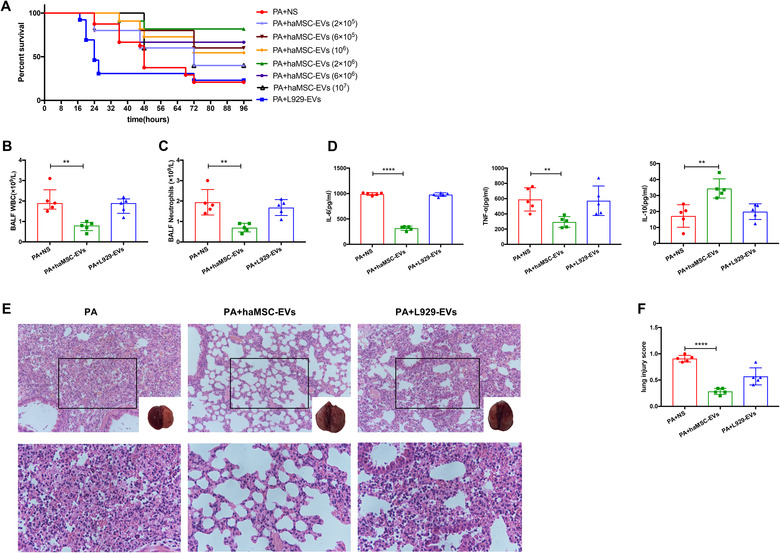
Therapeutic effects of haMSC‐EVs in P. aeruginosa‐induced murine lung injury model. (a) Kaplan‐Meier survival curves of P. aeruginosa‐induced murine lung injury model (N = 10 per group). (b‐c) Aerosol inhalation of haMSC‐EVs post‐infection decreased the influx of white blood cells (P = 0.0026, ** indicates P < 0.01, 2.0 ± 0.3 for PA + NS, 0.8 ± 0.1 for PA + haMSC‐EVs, N = 5) and neutrophils (P = 0.0029, ** indicates P < 0.01, 1.9 ± 0.3 for PA, 0.7 ± 0.1 for PA + haMSC‐EVs, N = 5) in BALF at 24 h. (d) The BALF levels of IL‐6 (**** indicates P < 0.0001, 990.1 ± 12.3 for PA + NS, 316.3 ± 18.9 for PA + haMSC‐EVs, N = 5), TNF‐α (P = 0.0044, ** indicates P < 0.01, 589.9 ± 68.4 for PA + NS, 294.8 ± 31.7 for PA + haMSC‐EVs, N = 5) were decreased in haMSC‐EVs group. The level of IL‐10 expression was increased (P = 0.0032, ** indicates P < 0.01, 17.2 ± 3.1 for PA + NS, 34.4 ± 2.7 for PA + haMSC‐EVs, N = 5) in haMSC‐EVs group. (e) The histology showed less inflammatory cells infiltrating interalveolar septa and respecting alveolar space and lung architecture. (f) Aerosol inhalation of haMSC‐EVs post‐infection also reduced histological severity of lung injury better than other groups (**** indicates P < 0.0001, 0.908 ±0.03 for PA + NS, 0.284 ± 0.03 for PA + haMSC‐EVs, N = 5). haMSC‐EVs: human adipose‐derived MSC‐Extracellular vesicles; PA: P. aeruginosa; L‐929‐Exos: NCTC clone 929 cells derived exosomes; BALF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; WBC: white blood cell; IL‐6: interleukin 6; TNF‐α: tumour necrosis factor‐α; IL‐10: interleukin 10
