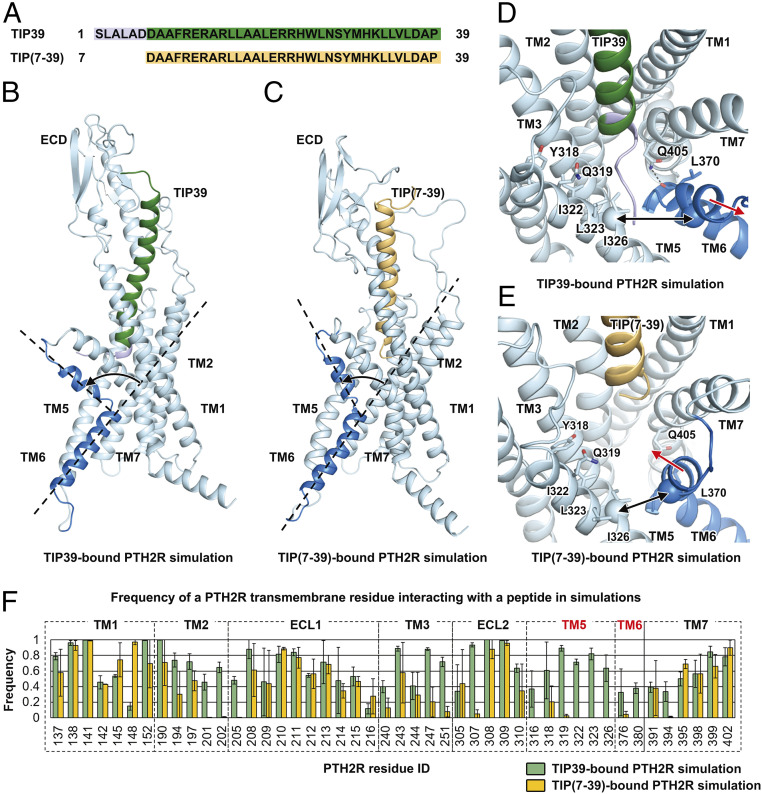
Fig. 4.
Molecular mechanism of the TIP(7-39) antagonism at PTH2R. (A) Sequence alignment between TIP39 and TIP(7-39). (B) A representative snapshot from the TIP39-bound PTH2R simulation system showing a TIP39-induced conformational change of the TM6 helix. (C) A representative snapshot from the TIP(7-39)-bound PTH2R simulation system showing a TIP(7-39)-induced conformational change of the TM6 helix. (D) A representative snapshot from the TIP39-bound PTH2R simulation system showing the N terminus of TIP39 insertion between TM5 and TM6 helices. Key residues are shown as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. The Cα atoms of residues Ile3265.47b and Ile3776.54b are shown as spheres. (E) A representative snapshot from the TIP(7-39)-bound PTH2R simulation system showing a conformational change of the TM6 helix. (F) Frequency of a PTH2R residue interacting with TIP39 (green) or TIP(7-39) (yellow) in simulations. The frequency value suggests the stability of a particular residue–peptide interaction. A large interacting frequency suggests a stable interaction.