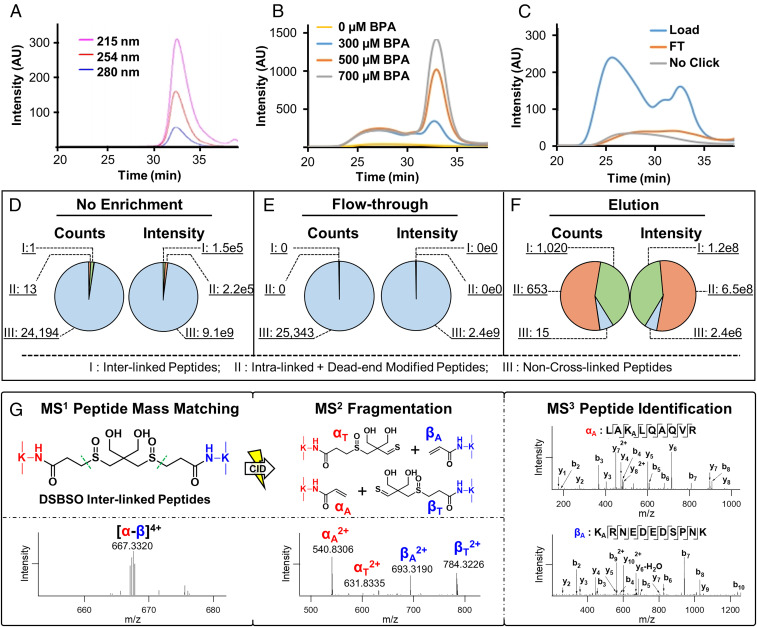
Fig. 2.
Enrichment and analysis of Alkyne-A-DSBSO cross-linked peptides. (A) SEC separation and detection of free BPA at three wavelengths: 215, 254, and 280 nm. (B) Assessment of biotin conjugation efficiency of Alkyne-A-DSBSO cross-linked peptides with increasing amounts of BPA monitored at 254 nm by SEC. (C) Evaluation of purification efficiency of BPA-labeled cross-linked peptides before binding to streptavidin beads (load) and flow through (FT) after binding through SEC. This process was monitored by comparing peptide UV absorbance at 254 nm. Unlabeled cross-linked peptides were used as control. (D–F) Benchmarking of cross-link enrichment performance using cross-linked cell lysates. Comparative analysis was performed among nonenriched (original), FT after binding of BPA-labeled cross-linked peptides to streptavidin beads, and elution (enriched cross-linked peptides) samples. Note: counts describe the total number of identified peptides, and intensity represents the total ion intensity of each defined group. Three groups of peptides in each sample were identified and compared: I, interlinked peptides; II, intralinked + dead-end modified peptides; and III, non–cross-linked peptides. (G) MSn analysis of a representative DSBSO interlinked peptide (α-β). The parent ion mass (m/z 667.33204+) was detected in MS1, which produced two characteristic fragment ion pairs modified with complementary DSBSO remnants, that is, αA/βT (m/z 540.83062+/784.32262+) and αT/βA (m/z 631.83352+/693.31902+) using collision-induced dissociation (CID) during MS2 analysis. Subsequent MS3 analyses of individual fragment ions αA (m/z 540.83062+) and βA (m/z 693.31902+) yielded series of b and y ions that identified them as 55LAKALQAQVR63 of BTF3 and 91KARNEDEDSPNK101 of RPL31, respectively. The integration of MS1, MS2, and MS3 data accurately determined a cross-link between BTF3:K57 and RPL31:K91. Note: KA represents alkene modified lysine.