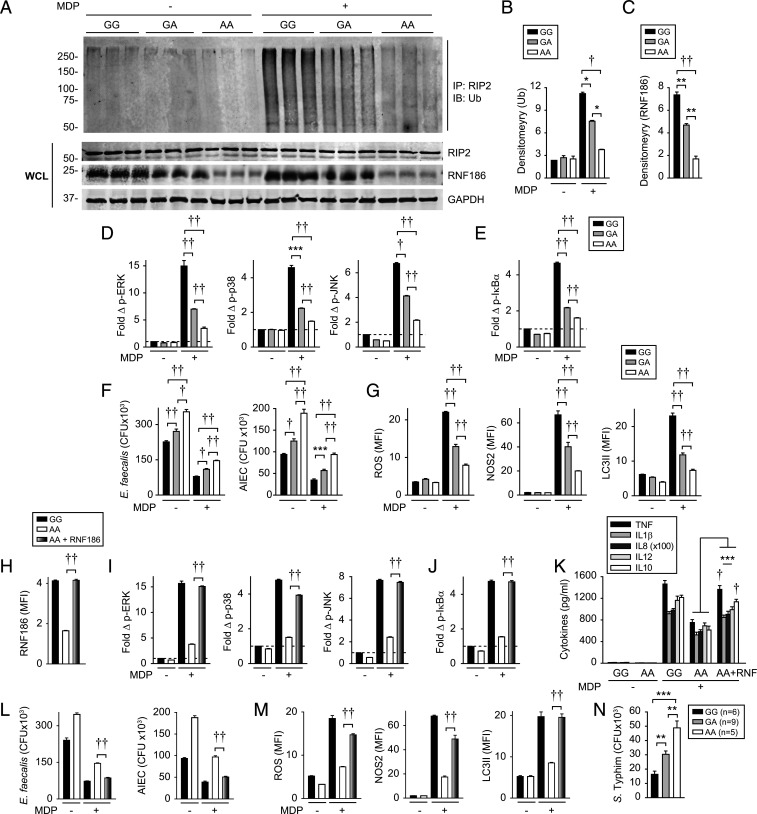
Fig. 7.
IBD-risk rs6426833 A carriers show reduced NOD2-induced ubiquitination, signaling, and antimicrobial pathways. (A–C) MDMs from rs6426833 GG, GA, or AA carriers were left untreated or treated with 100 μg/mL MDP. (A) RIP2 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and ubiquitinated proteins (Ub) were assessed by Western blot at 45 min (shown is n = 3 donors/genotype). WCLs were assessed for loading controls. (B) Densitometric analysis of ubiquitinated complex from top 50 kDa from A (n = 6 donors/genotype). (C) Densitometric analysis of RNF186 expression from A. (D–G) MDMs from rs6426833 GG, GA, or AA carriers (n = 10 donors/genotype; similar results in additional n = 16 donors/genotype) were treated with 100 μg/mL MDP. (D and E) Fold phospho-proteins at 15 min. At 48 h (F and G), cells were assessed for intracellular bacterial clearance (F) and antimicrobial pathways (G). (H–M) MDMs from rs6426833 GG or AA carriers (n = 10 donors/genotype) were transfected with EV or RNF186-expressing vector. (H) RNF186 expression. Cells were then treated with 100 μg/mL MDP. (I and J) Fold phospho-proteins at 15 min. (K) Cytokines at 24 h. At 48 h (L and M), cells were assessed for intracellular bacterial clearance (L) and antimicrobial pathways (M). (N) Intracellular bacterial clearance in human intestinal myeloid cells stratified on rs6426833 genotype. Mean + SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; †P < 1 × 10−4; ††P < 1 × 10−5.