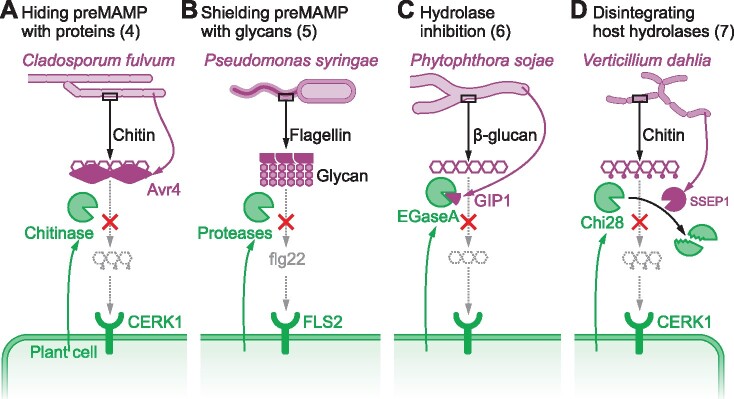
Figure 3.
Four mechanisms to avoid hydrolytic MAMP release (Level 2). A, Example of Strategy 4: the fungal tomato pathogen C. fulvum prevents the release of chitin fragments by secreting Avirulence protein-4 (Avr4) to hide chitin in the cell wall from hydrolysis by plant-secreted chitinases. B, Example of Strategy 5: the bacterial tobacco (N. tabacum) pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci 6605 prevents the proteolytic release of the flagellin elicitor flg22 by carrying a glycan covering the flagellin polymer. C, Example of Strategy 6: The oomycete soybean pathogen Phytophthora sojae prevents the release of β-glucan-based elicitors by secreting glucanase inhibiting protein-1 (GIP1), which inhibits the plant-secreted endoglucanase EGaseA. D, Example of Strategy 7: the fungal cotton pathogen V. dahlia prevents the release of immunogenic chitin fragments by Secreting Serine Protease (SSEP1), which inactivates host-secreted chitinase Chi28.