Figure 1.
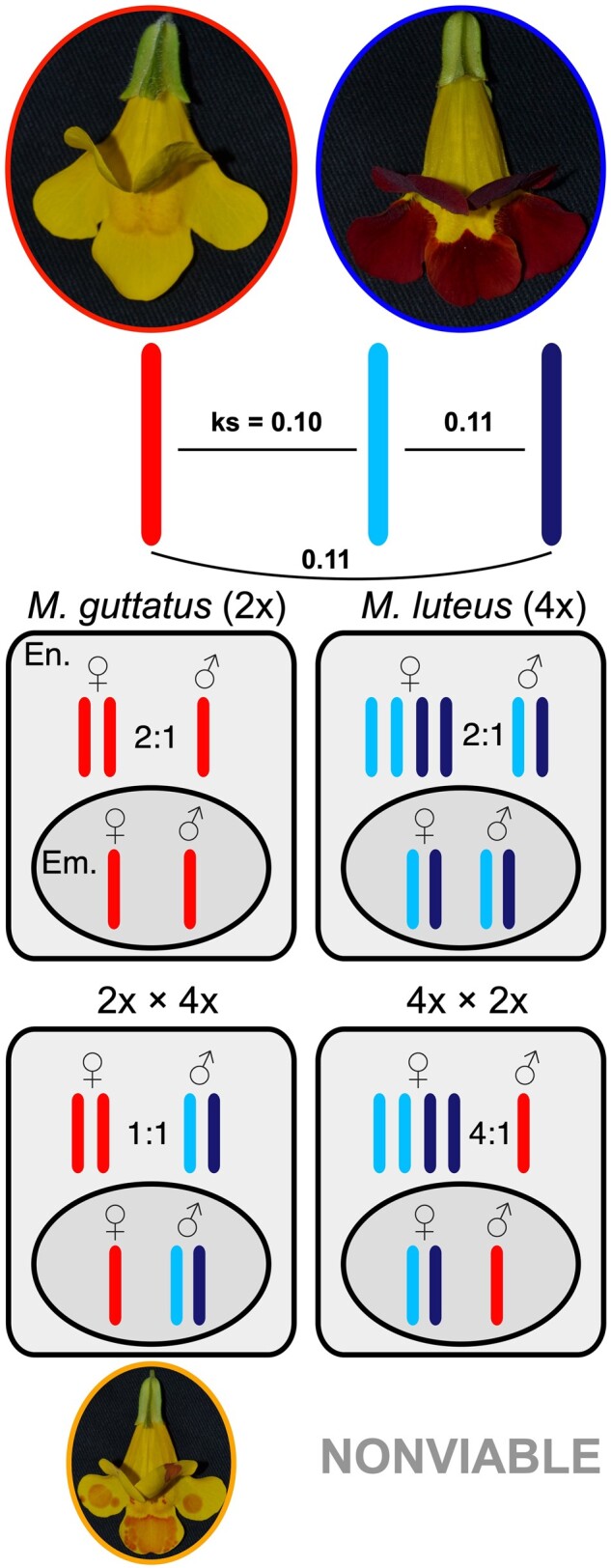
The Mimulus guttatus × M. luteus hybridization system. M. guttatus (in the red oval; left) is a diploid and M. luteus (in the blue oval; right) is a tetraploid with two distinct subgenomes (light blue and navy). Pairwise synonymous site divergences (ks) between the two M. luteus subgenomes and between each of them and M. guttatus are provided. Within seeds for each species, the genomic ratio between parental alleles is 2 maternal:1 paternal in the endosperm (En.) and 1:1 in the embryo (Em.), despite the tetraploidy of M. luteus. When hybridized, if M. guttatus is the maternal progenitor, the genomic ratio between parental alleles is 2:2 (1:1) in the endosperm, and seeds are often viable (M. × robertsii; orange). However, if M. luteus is the maternal progenitor, the ratio is 4:1 and seeds are almost always nonviable. Within the hybrids there are three distinct subgenomes (one from M. guttatus and two from M. luteus—colors are shown throughout).
