Figure 8.
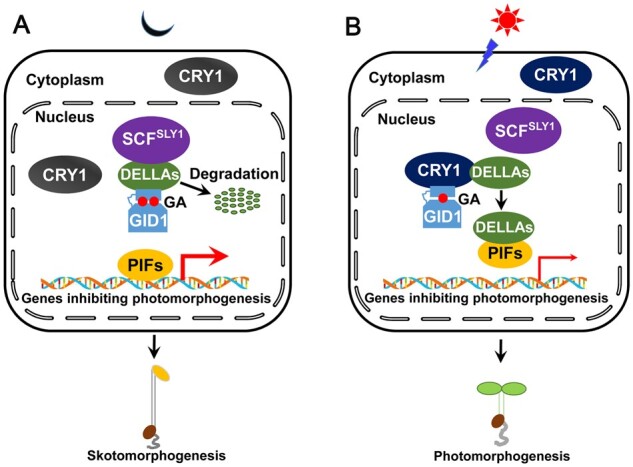
A model illustrating how CRY1 inhibits GA-induced degradation of DELLA proteins and GA signaling. A, B, In the dark, CRY1 is inactive and unable to interact with GID1 or DELLA proteins. GA triggers the interaction of GID1 with DELLA proteins (DELLAs), which are then targeted by SCFSLY1 for ubiquitination and degradation through the 26S proteasome. PIFs are released from the repression of DELLA proteins, and bind to the promoters of their target genes to inhibit photomorphogenesis, and promote their expression and skotomorphogenesis (A); upon blue light illumination, CRY1 is activated and regulates the expression of GA metabolism genes to reduce GA levels. At the same time, CRY1 interacts with GID1 and DELLAs to impair the interaction of DELLAs with SLY1 and GID1. DELLA proteins accumulate and interact with PIFs to inhibit their DNA-binding activity, leading to the inhibition of the expression of genes repressing photomorphogenesis and the promotion of photomorphogenesis (B). Thick and thin red arrows denote gene expression being induced and repressed, respectively. Two (in the dark) and one (in the light) red solid circles denote more and less GA levels, respectively.
