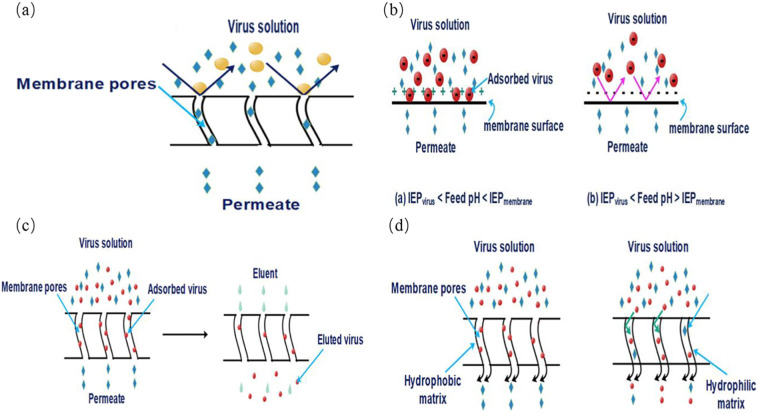
Fig. 5.
Schematic illustration of virus removal in membrane separation: (a) size exclusion, performing a dominant removal efficiency when the size of virus particles is bigger than the nominal pore size of membranes, (b) electrostatic interactions that is more prone to be affected by the PH of feed water, (c) adsorption and elution, and (d) hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions that are highly influenced by the properties of membrane material and virus particles (Goswami and Pugazhenthi, 2020).