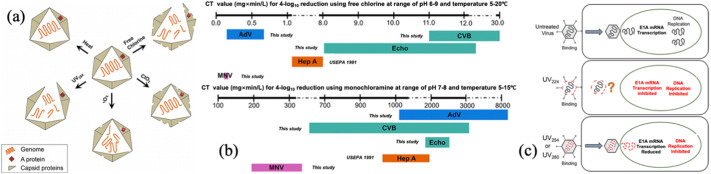
Fig. 8.
(a) Principle of different disinfections for damaging the virus structure. UV irradiation and free chlorine caused inactivation primarily by damaging both viral genome and protein, 1O2 caused inactivation by impairing genome replication and ClO2 by the degradation of proteins (Wigginton et al., 2012); (b) CT values needed to achieve 4 LRVs of the removal of AdV, CVB, ECHO and MNV using free chlorine at pH 6–9 and temperature 5–20 °C (above) and using monochloramine at pH 7–8 and temperature 5–15 °C (below) (Rachmadi et al., 2020); (c) distinctive inactivation mechanism of UV radiation at different wavelengths. UV224 mainly affected the integrity of viral capsid to inhibit the delivery of viral genome into the host cell, while UV254 and UV280 mainly restrained the DNA replication (Bravo et al., 2018).