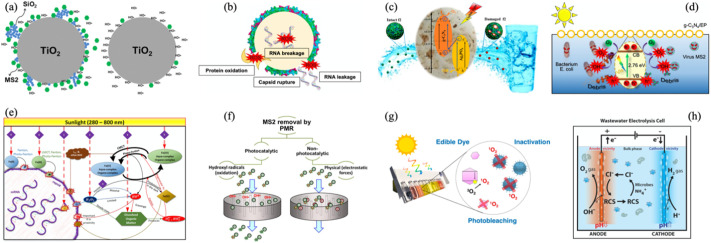
Fig. 9.
(a) Photocatalytic inactivation of TiO2 toward bacteriophage MS2 with (left) and without (right) the addition of SiO2 nanoparticles (Liga et al., 2013); (b) response of viral death to g-C3N4-based photocatalytic disinfection including protein oxidation, capsid rupture, RNA breakage and RNA leakage (Zhang et al., 2019a); (c) a possible Z-scheme inactivation mechanism of bacteriophage f2 by Ag3PO4-g-C3N4 photocatalytic material. The f2 was oxidized by photogenerated holes (h+) under visible light irradiation, together with hydroxyl radicals (•OH) formed by reaction between h+ and H2O or OH− near the surface of Ag3PO4 and superoxide radical (•O2−) caused by trapping electrons by dissolved oxygen near the surface of g-C3N4 (Cheng et al., 2018); (d) proposed mechanism of bacteriophage MS2 inactivation by g-C3N4-EP520 under visible-light irradiation (Zhang et al., 2018); (e) proposed MS2 inactivation route during the photo-Fenton process through (1) direct sunlight, (2) oxidative stress exerted by H2O2, (3) irradiation of the DOM to generate H2O2, O2−, 1O2 and other ROS, (4) enhancement of the •OH production under solar light in Fenton reaction, (5) aquo-complexes by hydrolysis and organo-complexes in the presence of DOM for Fe(III) in the wastewater and (6) organo-complexes from the interaction of Fe(II) and Fe(III) with amino acids in MS2 capsid (Giannakis et al., 2017); (f) process of bacteriophage MS2 removal by PMR (including the oxidation of hydroxyl radicals in photocatalytic and electrostatic force in non-photocatalytic) (Horovitz et al., 2018); (g) enhanced solar disinfection method using an edible dye as a photosensitizer to generate 1O2 for virus inactivation and signify the finish of solar disinfection by photobleaching (Ryberg et al., 2018); (h) a electrolysis cell for toilet wastewater disinfection in which the free reactive chlorine produced in situ instead of •OH and other reactive oxygen species was the main disinfection ingredient (Huang et al., 2016).