Figure 9.
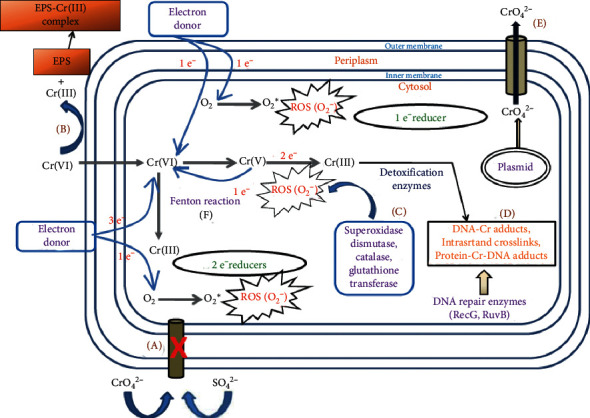
Chromate resistance mechanism in bacteria. (A) Mutation in sulfate uptake transporters. (B) Extracellular reduction of Cr6+ to Cr3+. (C) Intracellular reduction of Cr6+ to Cr3+ by chromate reductase. (D) Reducing oxidative stress and activation of repairing systems. (E) Outflowing of chromate from the cytoplasm. (F) Decreasing oxidative stress by activation of ROS scavenging enzyme. Adapted from [14].
