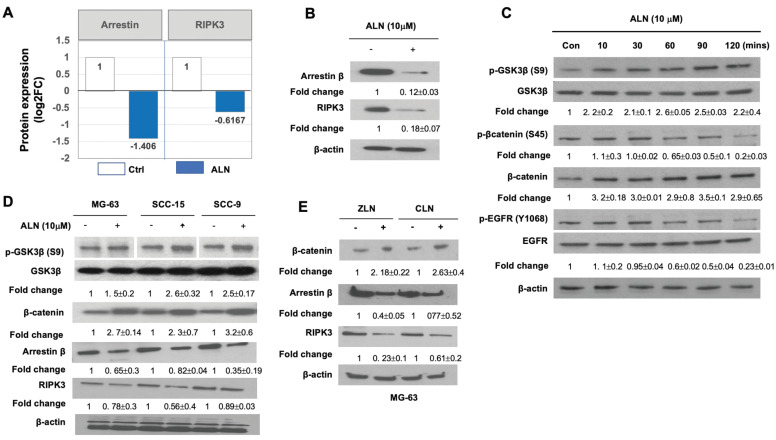
Figure 3.
The RIPK3/arrestin/GSK3β/ β-catenin/VEGF pathway is altered by ALN treatment. (A-B). Quantification results showed that arrestin β and RIPK3 are significantly suppressed with ALN treatment. (A) Data from proteomics profiling. DEP levels obtained from proteomics analysis are shown in Table 1. (B) Western blot analysis to measure the expression levels of arrestin β and RIPK3 proteins in the presence or absence of ALN. β-actin was used as the loading control. (C) ALN-induced phosphorylation of GSK3β (S9) and β-catenin (S45) led to stabilization of β-catenin in MG-63 cells. (D) Comparison of phosphorylation of GSK3β and expression of β-catenin, arrestin β, and RIPK3 in MG-63, SCC-15, and SCC-9 cells after treatment with ALN. (E) Effects of several BPs (ZLN and CLN) on β-catenin, arrestin β, and RIPK3 in MG-63 cells. After stimulation with 10 μM of ALN, ZLN, or CLN at various times, cells were harvested for protein extraction and western blot analysis. Representative western blot images were selected after experiments were repeated 6 times.