Figure 1.
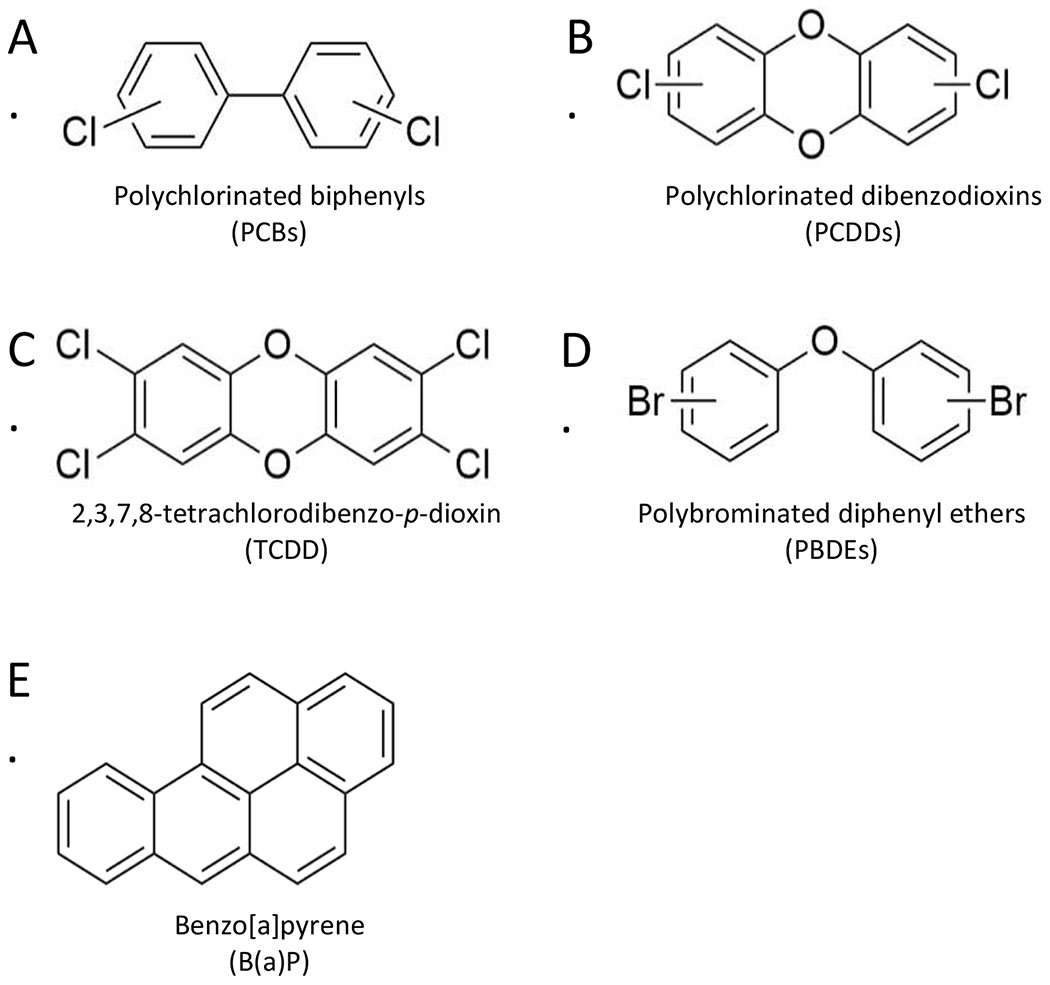
Chemical structures of common persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Many POPs including (A) polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), (B) polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs) including (C) the most toxic PCDD congener 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), and (D) polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are carbon-based compounds with high-molecular weight, high lipid solubility, and varying degrees of halogenation. These chemical properties confer resistance to chemical and biological degradation, allowing for bioaccumulation of these pollutants in lipid-rich body tissues, including the brain, even at low doses. (E) Benzo(a)pyrene lacks the typical halogen substitutions but is equally lipid soluble and resistant to biodegradation. Figure was created with ChemDraw software.
