Figure 2. Neutralization of spike S1 by nanodecoys.
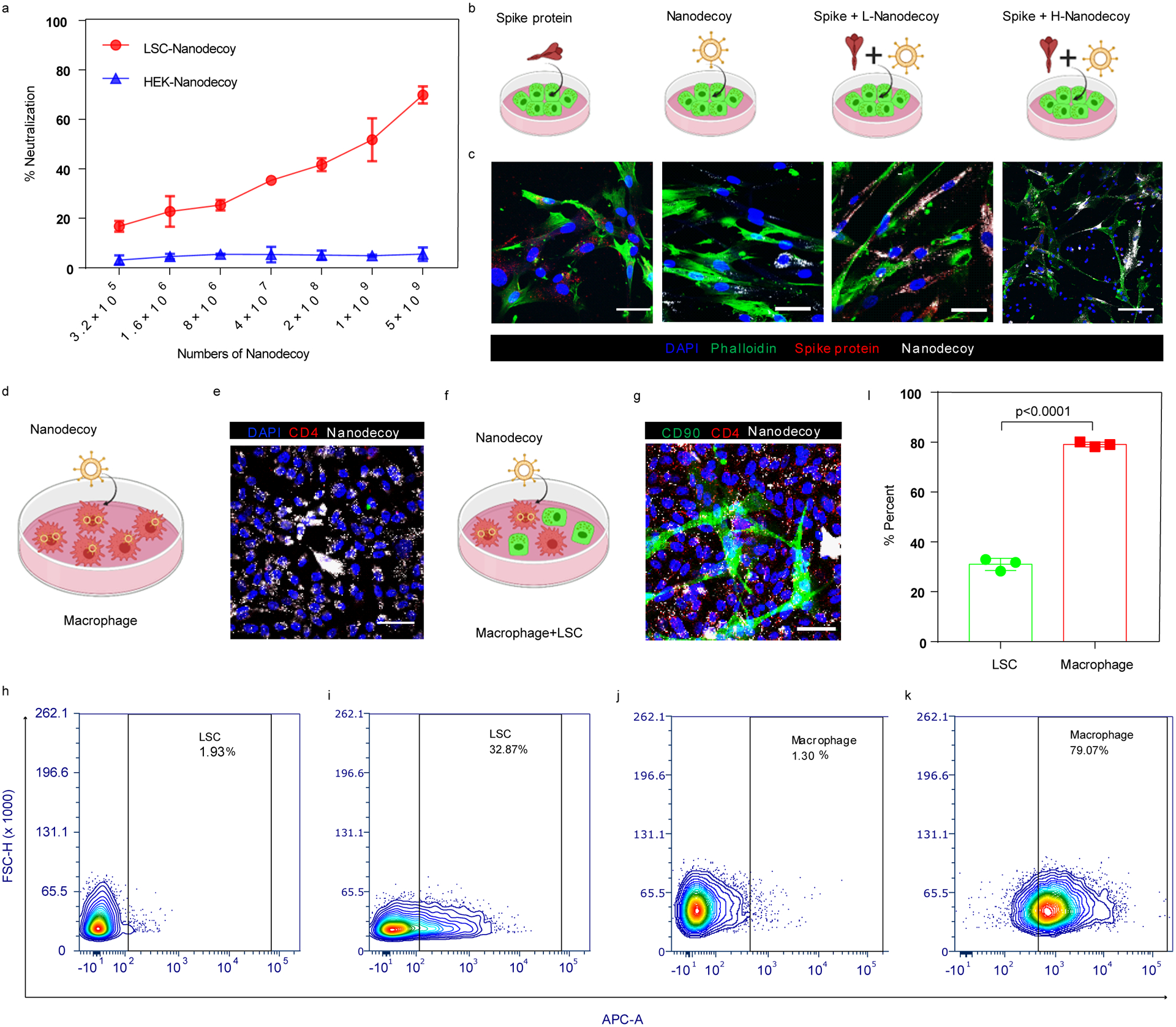
(a) Dose-dependent neutralization of spike S1 by LSC-nanodecoys or HEK-nanodecoys. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n=3 independent experiments. (b) Schematic illustrating the experimental design. (c) Interaction of spike S1 (red) and nanodecoys (white) when co-cultured with lung cells (green). (d) Schematic illustrating the experimental design. (e) Representative confocal images showing internalization of nanodecoys by macrophages (CD4, red). Four images were taken. (f) Schematic illustrating the co-culture experiment and (g) confocal images of the internalization of nanodecoys by macrophages co-cultured with lung cells (CD90, green). Flow cytometry analysis showing internalization of DiD-labeled nanodecoys by LSCs (i) and macrophages (k) and (l) its corresponding quantitation. PBS was used as control group for LSCs (h) and macrophages (j). See Supplementary Figure S18a for gating strategies. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n=3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with two-tailed Student t-test. Scale bars, 50 μm for Figure 2c, 2e and 2g. Cartoon pictures were created with BioRender.com.
