Figure 1. Responses of NK cells that contribute to vaccine efficacy.
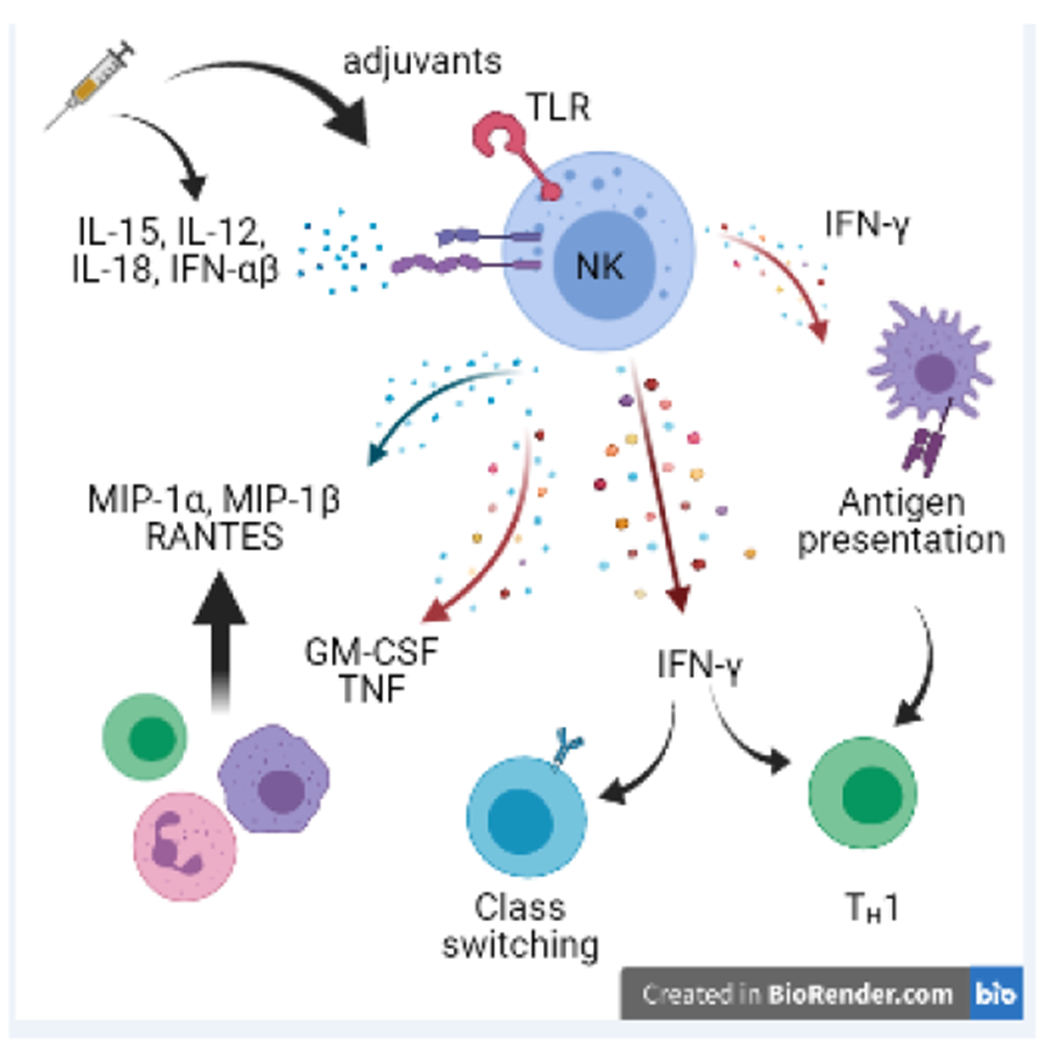
Vaccination can trigger NK cell activation via direct engagement of receptors on NK cells (e.g. adjuvant binding to TLR4) or via triggering of expression of IL-12, IL-18, and type I IFN. Activated NK cells produce IFN-◻, thereby promoting TH1 differentiation of CD4 T cells, IgG2a class switching by B cells, and enhancing antigen presenting functions of myeloid cells. NK cells make cytokines (e.g. GM-CSF) and chemokines (e.g. MIP-1◻) that facilitate recruitment of myeloid cells, granulocytes, and other lymphocytes.
