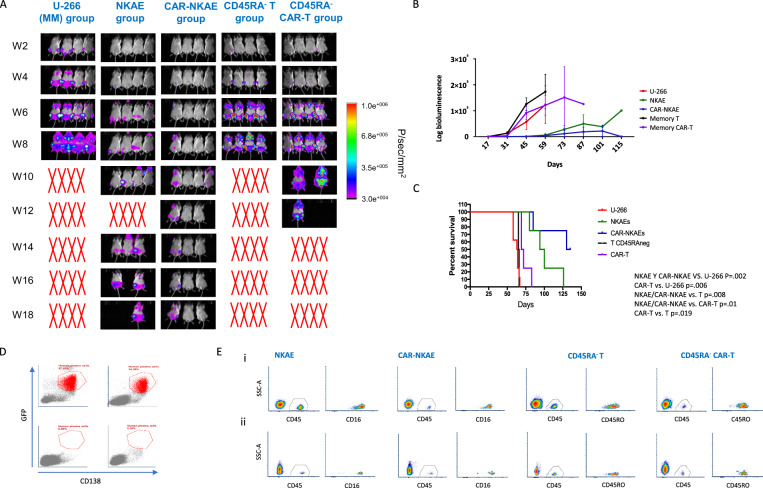
Fig. 7. NKG2D-CAR-transduced NKAE cells exhibit potent efficacy in vivo.
A Imaging of tumor burden monitored by bioluminescence at the indicated timepoints in MM mice, NKAE-cell-treated mice, and CAR-NKAE-cell-treated mice (At day 73 mice 2 and 3 from NKAE group were accidentally interchanged). B Quantification of the bioluminescence signal in MM mice, NKAE-cell-treated mice, CAR-NKAE-cell-treated, CD45RA− T-cell-treated mice and CD45RA− T-cell-treated mice at the indicated timepoints and C Kaplan–Meier survival curves. D Representative flow cytometry dotplots showing bone marrow infiltration (GFP+ CD138+) of MM mice (top left), NKAE-cell-treated mice (top right), and the two CAR-NKAE-treated mice that were disease free at the end of the study (bottom). E Persistence of effector cells in peripheral blood (i) 10 days after infusion and (ii) 20 days after infusion. Representative flow cytometry density plots for NKAE/CAR-NKAE cells that were identified by human CD45 and CD16 labelling and for CD45RA− T/CAR-T cells that were identified by human CD45 and CD45RO labelling.