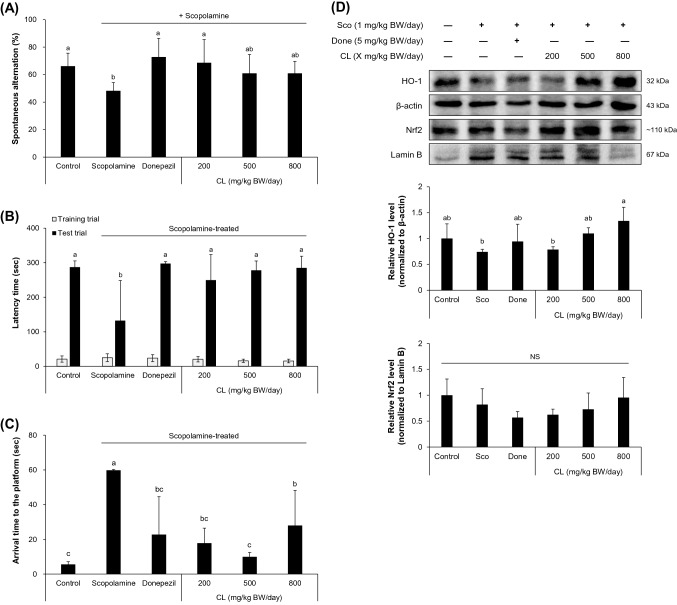
Fig. 1.
CL administration improved scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment. Freeze-dried CL powder was dissolved in a vehicle (5% (v/v) Tween 80 in sterilized saline) and orally administered to C57BL/6J mice at designated doses. Scopolamine was intraperitoneally injected at 1 mg/kg BW/day 30 min after CL administration to induce memory impairment. (A–C) Memory improvement was assessed by the Y-maze task (A), passive avoidance task (B), and Morris water maze task (C). Values presented are means ± standard deviation (SD) from eight individual animals (n = 8) for (A) and n = 6 after the removal of outliers for (B–C). (D) Cytoplasmic HO-1 and nuclear Nrf2 protein levels were examined in the hippocampal tissue homogenates. Donepezil (5 mg/kg BW/day) was used as positive control. Sco, scopolamine; Done, donepezil; CL, Ceriporia lacerata; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2. Values are means ± SD (n = 5). Different letters on the bars (a–b) denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.05). NS indicates no statistically significant difference among experimental groups