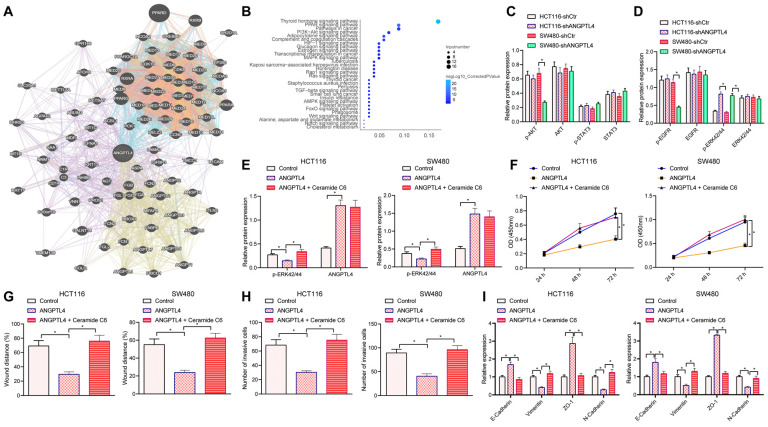
Figure 4.
ANGPTL4 knockdown regulated the migration, invasion, and EMT of CRC cells by activating ERK signaling pathway. (A) ANGPTL4-related genes were predicted in-silico, and each circle indicates a gene and the line between circles indicates an association between genes. (B) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of ANGPTL4-related genes, wherein the x-axis indicates Gene Ratio, y-axis indicates KEGG items, the circle size indicates the number of genes enriched in the items, the circle color indicates the enrichment p value, and the right histogram is the color scale. (C) Western blot analyses to detect the activation status of p-AKT/AKT and p-STAT3/STAT3 after ANGPTL4 knockdown. (D) Western blot analysis to detect the activation status of p-EGFR/EGFR and p-ERK42/44/ERK42/44 after ANGPTL4 knockdown. (E) Western blot analysis to detect the expression level of p-ERK42/44 in HCT116 cells and SW480 cells after ANGPTL4 or Ceramide C6 treatment. (F) CCK8 assay to quantify cell proliferation. (G) Wound healing assay to determine the cell migration ability. (H) Transwell assay to determine cell invasion ability. (I) RT-qPCR to determine the mRNA expression levels of EMT-related proteins in CRC cells. (J) Western blot assay to determine the expression level of EMT-related proteins. * p < 0.05.