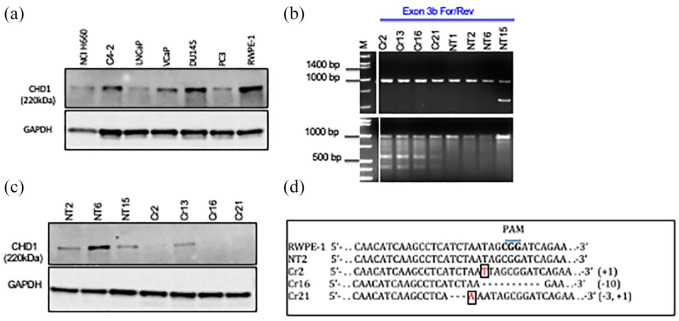
Figure 1.
Generation of RWPE-1 CHD1 KO line. (a) Western blot showing CHD1 expression across a panel of prostate cancer cell lines (NCI H660, C4-2, LNCaP, VCap, DU145 and PC3) and the normal prostate epithelial cell line, RWPE-1. CHD1 expression is highest in RWPE-1 as compared to the cancer cell lines which show variable levels of CHD1. (b) Top panel: Gel run image representative of genomic PCR products from clones targeted with sgRNA designed for the CHD1 gene (Cr2, Cr13, Cr16, Cr21) and with the non-target vector control (NT1, NT2, NT6, NT15). The Exon 3b forward and reverse primers used, amplified a 1 kb region in exon 3 of the CHD1 gene that includes the sgRNA sequence upstream of the PAM sequence and the Cas 9 target sequence. Once Cas9 enzyme makes sgRNA/PAM specified cuts in the genomic DNA, the DNA repair process of nonhomologous end joining can cause insertions and or deletions in the DNA leading to presence of heteroduplexes along the DNA double strand. T7 endonuclease is known to nick dsDNA in heteroduplex regions. Bottom panel: Gel run of products resulting from digestion of the 1 kb genomic PCR product with T7 endonuclease, following denaturation and reannealing. Cr2, Cr13, Cr16 and Cr21 show the additional low molecular weight fragments representative of heteroduplex formation resulting from insertions/deletions. NT1, NT2, NT6 and NT15 show only a 1 kb product indicating that SgRNA/PAM based specific Cas9 digestion has not taken place in the non-target controls. (c) Western blot confirming CHD1 expression in NT2, NT6, and NT15 and loss of expression in Cr2, Cr16, and Cr21. Cr13 showed expression of CHD1. (d) Clones were subsequently confirmed as wildtype or mutant through Sanger sequencing. RWPE-1 and NT2 showed the wildtype CHD1 sequence. Cr2 and Cr21 showed an insertion of T and A, respectively, shown in boxes. Cr21 showed a 3-base deletion, demonstrated as dashes. Cr16 demonstrated a 10-base deletion, shown as dashes.
CHD1, chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; NT, non-target cells; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif; sgRNA, small guide RNA.