Figure 5.
Defective Cebpg KO NK cells exhibit milder effects on HSC function than WT NK cells
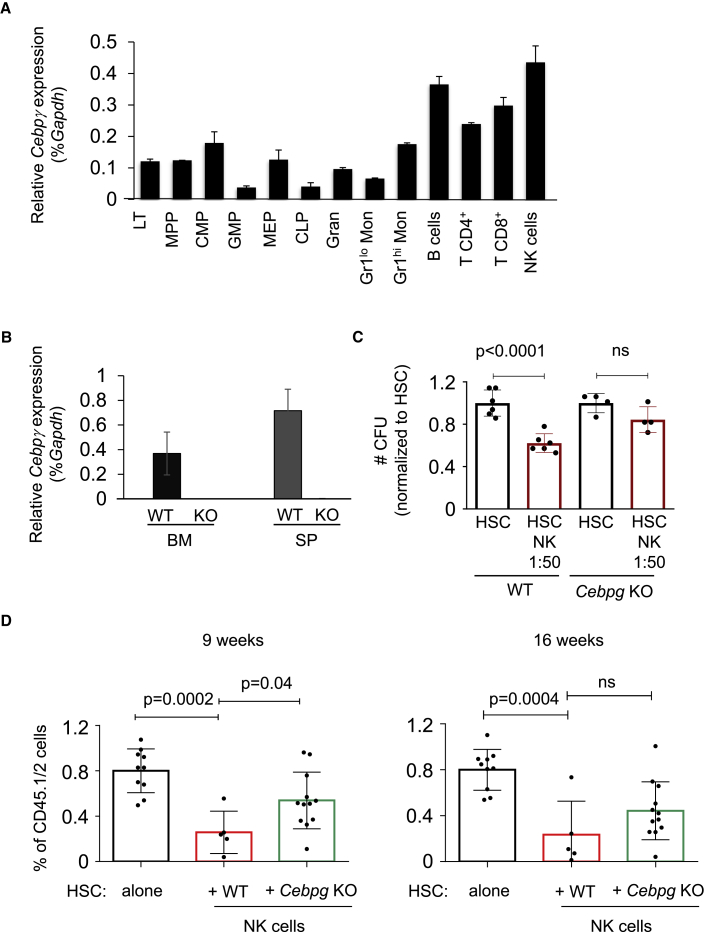
(A) Relative Cebpg expression levels shown as the percentage of Gapdh (% Gapdh) in distinct sorted hematopoietic cell populations. LT (long-term HSC), MPP (multi-potent progenitor), CMP (common myeloid progenitor), GMP (granulocyte-macrophage progenitor), MEP (megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor), CLP (common lymphoid progenitor), Gran (granulocyte), Gr1lo Mon (Gr1lo monocyte), Gr1hi Mon (Gr1hi monocyte), B cells, T CD4+ cells, T CD8+cells, and NK cells.
(B) Cebpg mRNA levels in BM and SP isolated from WT and Cebpg KO mice. Y axis indicates relative Cebpg expression levels relative to Gapdh (% Gapdh).
(C) Colony culture assays of murine cells. Y axis indicates the number of CFU relative to HSC condition. X axis indicates culture conditions: HSC alone or in the presence of WT or Cebpg KO NK cells. Cell ratio is indicated. Each dot represents one culture dish. Data represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
(D) Engraftment of CD45.1/2 cells in blood of recipient CD45.1 mice evaluated 9 (left) and 16 weeks (right) after transplantation. X axis indicates transplant conditions where purified HSCs alone or with WT or Cebpg KO NK cells were co-cultured overnight in the presence IL-2 prior to transplantation. Y axis demonstrates the percentage of CD45.1/2 cells. Each dot indicates values for one animal. All data represent mean ± SD from two independent experiments. For (C) and (D), two-tailed Student's t test was used to assess statistical significance (p values are indicated; ns, not significant).
See also Figure S5.