Figure 5. Effects of chromatin structure and chromatin bound proteins on cGAS activation.
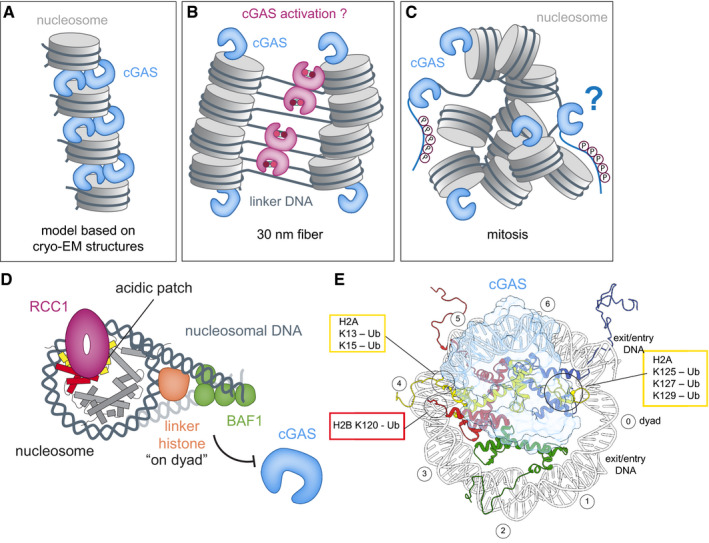
(A–C) Schematics of cGAS (blue) bound to nucleosomes (gray) based on cryo‐EM structure models (A), 30 nm‐fiber condensed‐chromatin model (B), and oligomers during mitosis (C). Accessibility of acidic patches determines whether cGAS is sequestered away from free linker DNA. During mitosis, cGAS is additionally inhibited through hyperphosphorylation of its N‐terminal region. (D) Chromatin‐binding factors, such as RCC1, BAF1, and linker histones, alter chromatin structure and compete with cGAS for binding sites. (E) Relation of important histone ubiquitylation sites on the nucleosome (disc view) to the cGAS‐binding site B.
