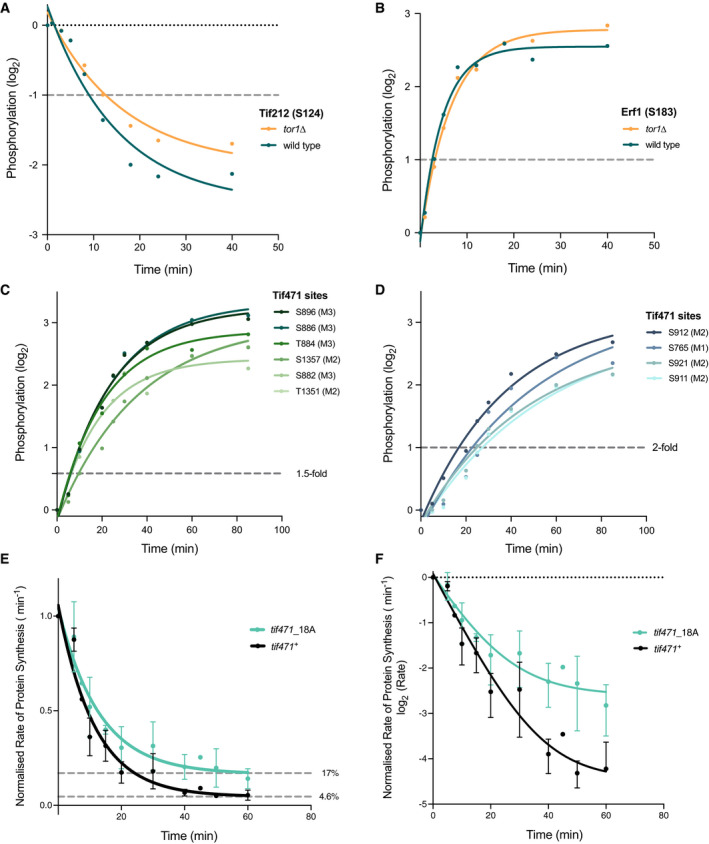
Phosphorylation kinetics of common phosphosites identified for 3 essential translation‐related proteins, and the effects of the
tif471_18A phosphosite mutant on rates of protein synthesis upon Torin1 treatment.
-
A, B
Phosphosites identified on (A) Tif212 and (B) Erf1, respectively, showing 2‐fold phosphorylation change within 20 min of Torin1 (5 µM) addition. Both wild type (green) and tor1∆ (yellow) phosphorylation values are relative to the starting phosphorylation levels before Torin1 addition in wild type cells (T = 0 min). Grey dashed lines indicate 2‐fold threshold.
-
C, D
Relative phosphorylation levels of the 10 common phosphosites of Tif471 plotted against time after Torin1 treatment. Phosphorylation profiles are grouped based on phosphorylation kinetics, where 6 sites showed more than 1.5‐fold increase by 10 min (C), and the remaining 4 exceeded 2‐fold by 30 min (D). Grey dashed lines indicate 2‐fold threshold.
-
E, F
Changes in rates of protein synthesis of the tif471_18A mutant compared to the wild type control (tif471
+) upon Torin1 (5 µM) treatment. Residual rates of protein synthesis after 60 min of Torin1 treatment was 17% for the tif471_18A phosphomutant and 4.6% for the tif471
+ control relative to starting levels in the respective strains. The two graphs represent the untransformed (E) and log2 transformed (F) rates respectively. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of data aggregated from three independent experiments.