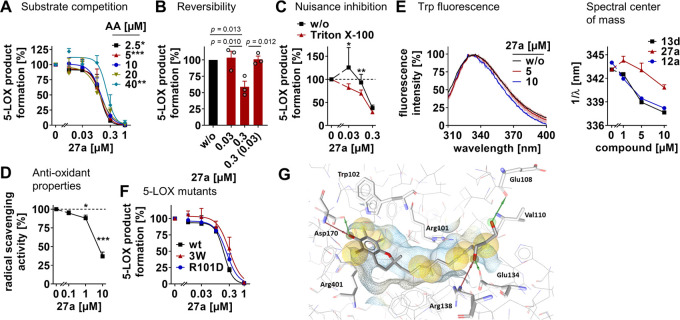
Figure 2.
Molecular insights into 5-LOX inhibition by 27a. (A) Effect of the arachidonic acid (AA) concentration on 5-LOX inhibition by 27a. (B) Reversibility of 5-LOX inhibition by 27a. Samples were preincubated with a vehicle or compound for 15 min, 10-fold diluted, and incubated for another 5 min before AA was added. The number in brackets indicates the diluted compound concentration after preincubation. (C) Effect of Triton X-100 (0.01%) on 5-LOX inhibition by 27a. (D) Scavenging of DPPH radicals by 27a. (E) Fluorescence excitation spectra as a percentage of maximum fluorescence intensity (left panel) and spectral center of mass of the fluorescence emission variations (right panel) shown for 5-LOX titrated with 13d, 27a, or 12a. (F) Effect of 27a on the inhibition of wild-type 5-LOX (wt), the triple mutant Trp13Ala, Trp75Ala, and Trp102Ala 5-LOX (3W), and the single mutant Arg101Asp 5-LOX (R101D). (G) Molecular docking pose of 27a in the allosteric binding site of 5-LOX showing the interaction with Asp170, Arg138, Glu134, and Glu108. Hydrogen bonds are shown as red (HBA) and green (HBD) arrows and hydrophobic contacts as yellow spheres. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (A–D, F) with single values (B) or mean ± SEM (transparent area) from n = 2 (E), n = 3 (A–C), and n = 4 (D, F) independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs 20 μM AA (A), control (D), absence of Triton X-100 (C), wt 5-LOX (F), or as indicated (B); two-way ANOVA + Tukey’s post hoc test (A, F), RM one-way ANOVA + Tukey’s post hoc test (B, D), two-tailed paired t-test of log data (C).