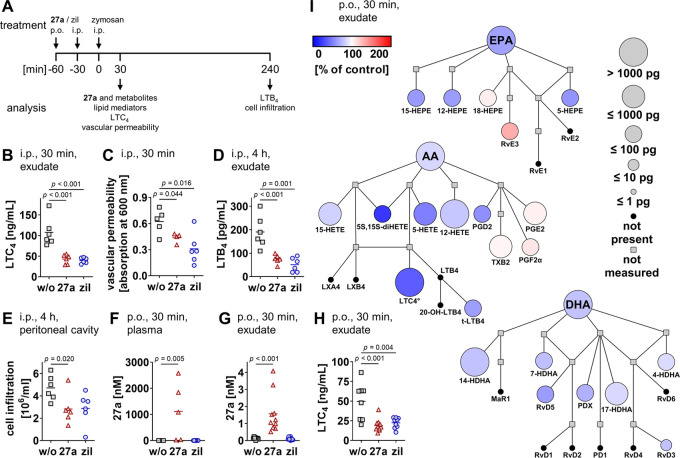
Figure 7.
Compound 27a inhibits 5-LOX product formation and limits inflammation in murine peritonitis. (A) Time scale for zymosan-induced murine peritonitis. (A–I) Mice received 27a (B–E, I: 10 mg/kg; F, G: 30 mg/kg; H: 3 mg/kg; B–E: i.p.; F–I: p.o.) or zileuton (zil; B–E: 10 mg/kg; F, G: 30 mg/kg; H: 3 mg/kg; B–E: i.p.; F–H: p.o.) and were killed 30 min (B, C, F–I) or 4 h (D, E) post zymosan injection. (B, H) LTC4 levels in the exudate analyzed by ELISA. (C) Vascular permeability. (D) LTB4 levels in the exudate analyzed by ELISA. (E) Immune cell infiltration into the peritoneal cavity. (F, G) Concentration of 27a in the plasma (F) and exudate (G). (I) Quantitative illustration of the lipid mediator network in the peritoneal exudate from mice given 27a as compared to the vehicle. The node size represents the mean concentration in pg, and the color intensity denotes the fold change for each lipid mediator. °LTC4 was analyzed by ELISA, and all other lipid mediators and fatty acids were analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS. AA, arachidonic acid; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; LX, lipoxin; MaR, maresin; 20-OH-LTB4, 20-hydroxy-LTB4; PD, protectin; Rv, resolvin; t-LTB4, LTB4 isomer; TX, thromboxane. Data are expressed as mean (I) with single values (B–H) from n = 3 (F, w/o), n = 4 (C, 27a), n = 5 (C, w/o, F, 27a), n = 6 (B, C, zil, D, E), n = 8 (H, w/o), n = 9 (G, w/o, H, zil, I, w/o), and n = 10 (F, zil, G, 27a and zil, H, 27a, I, 27a) mice. Two-tailed unpaired t-test of log data (B–H).