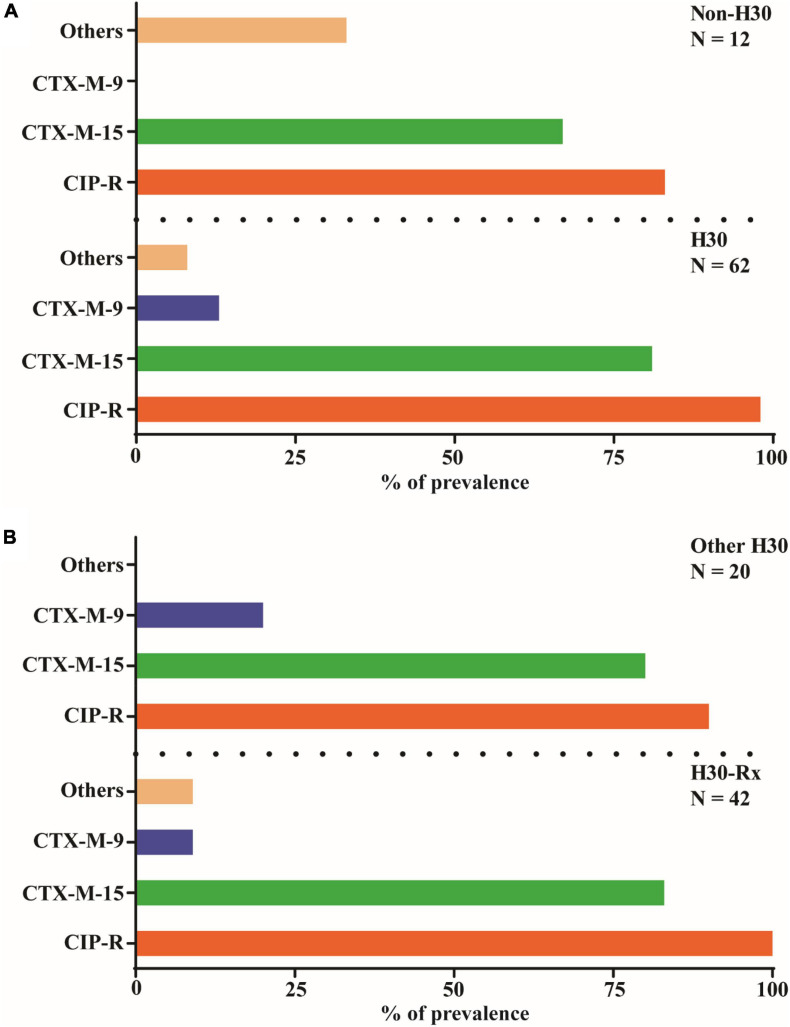
FIGURE 3.
Prevalence of key CTX-M genetic variants and ciprofloxacin resistance among 74 ST131 isolates. Note that as with all strains in this study the ST131 isolates were confirmed producers of β-lactamases as measured by resistance ampicillin (see Figure 2A). (A) All 74 ST131 isolates classified into H30 subclone (n = 62) and non-H30 subclone (n = 12). These 74 isolates were then tested for the prevalence of CTX-M gene distribution following PCR amplification and sequencing. Most of the isolates harboured either the gene encoding for the β-lactamase enzyme CTX-M-15 or CTX-M-9. A Pearson Chi-square test was used to evaluate if this distribution is statistically significant. The CTX-Ms distribution profile among the isolates of the two different groups were not significantly different (P > 0.05). (B) Of the 62 H30 isolates, 67.7% (n = 42) were identified as H30Rx using PCR. The vast majority of all isolates were ciprofloxacin resistant (CIP-R), CTX-Ms in group 1 other than CTX-M-9 or CTX-M-15 are classified collectively as “other.”