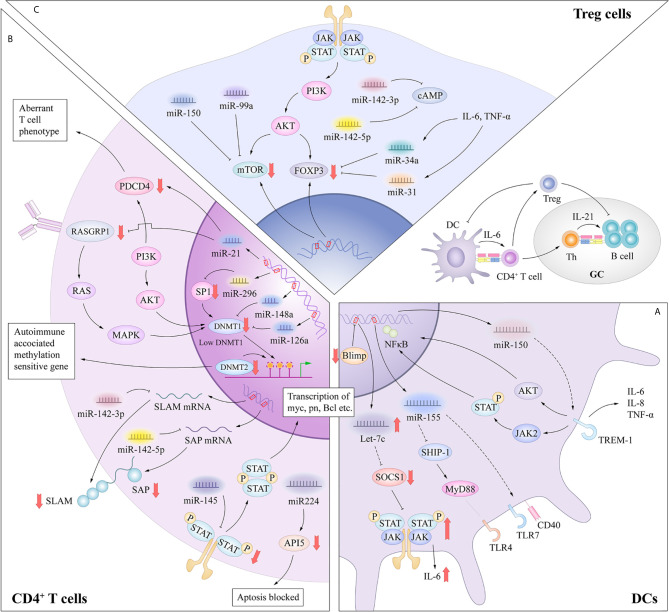
Figure 2.
(A) MiRNAs in dysfunctional antigen presentation by DCs. In the DC-specific absence of Blimp1, an increase in let-7 miRNA results in a broad spectrum of proinflammatory DC phenotype, mediated in part through suppression of SOCS1 expression. The CD40 expression was significantly upregulated with a negative correlation to the miR-155 in SLE primary target SHIP-1 expression. MiRNA-150 inhibited the expression of TREM-1 which amplify the function of TLR4. (B) miRNAs in aberrant activation of CD4+ T cells. MiR-21 contributed to the aberrant phenotype of T cells through interaction with PDCD4 or indirectly inhibiting DNMT1 expression through targeting RASGRP1. miRNAs such as miR-126, miR-29b and miR-148a can directly inhibit DNMT1 expression by targeting the protein coding region. These processes result in the overexpression of autoimmune-associated methylation-sensitive genes, which contribute to the autoreactivity and overstimulation of CD4+ T cells in SLE. miR-142-3p specifically targets the SLAM family, while miR-142-5p targets the 3’-UTR of SAP. Thus, decreased miR-142-3p/5p expression contributes to the up-regulation of CD84 and IL-10/SAP, resulting in the increased T cell function and IgG production in co-cultured B cells. Aberrant expression of miR-145 and miR-224 can promote T cell activation-induced cellular apoptosis and SLE-associated nephritis by overexpression of STAT1 and underexpression of API5. (C) miRNAs in functional inhibitory of Treg cells. The release of IL-6 or TNF-α can increase the expression levels of miR-34a, which can attenuate Foxp3 expression by targeting its 3ʹ-UTR. MiR-142-5p positively regulates intracellular levels of cAMP to maintain the suppressive function of Treg cells. MiR-142-3p can restrict cAMP levels in CD4+ T cells, which compromises the inhibitory function of Treg cells. MiR-99a and miR150 could regulate the function of Treg cells by targeting mTOR.