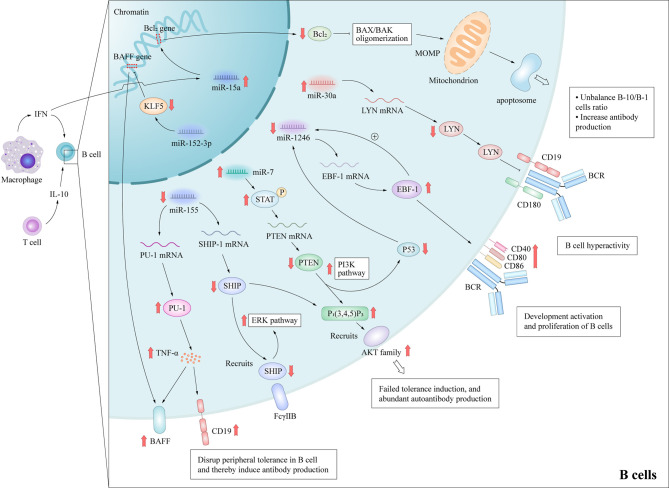
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms by which miRNAs promote B cell hyperactivity in SLE patients. These aberrant expressed miRNAs promote B cells abnormal activation and autoantibodies production in SLE by affecting important protein molecules in the B cell signaling pathway. MiR-15a interacts the Bcl-2 gene directly, which leads to the decrease of Bcl-2 and activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathway of regulatory B-10 cells. MiR-7 mediates the suppression of PTEN/AKT signaling, and then promotes B cell differentiation into plasma cells and spontaneous germinal center formation. Decreasing miR-155 in B cells contributes to the SHIP-1 reduction, which leads to the production of serum IgG anti-dsDNA antibodies. MiR-155 also suppresses PU.1 and TNF-α, and then inhibits BAFF and CD19 protein expression, and promotes the B cell proliferation and antibody production in SLE. MiR-30a increases in B cells of SLE patients and directly decreases the expression of Lyn, an important mediator of B cell activation, via targeting with the 3’-UTR of Lyn mRNA. MOMP, Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization; BAX/BAK, Bcl-2-associated X protein/Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer.