Fig. 2.
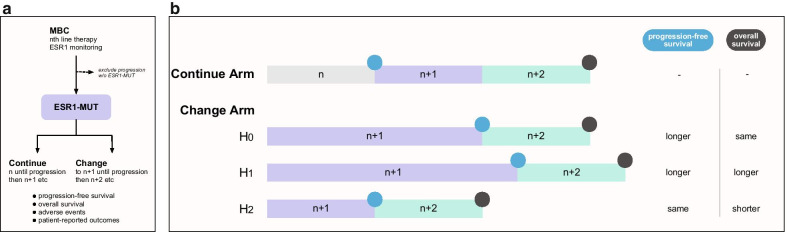
Trial design for testing the incorporation of ESR1 mutation monitoring into clinical decision-making. a Design. Patients with MBC start on standard treatment (such as AI plus CDK4/6i) with monitoring for the development of ESR1-MUT. Patients are excluded if they have clinical progression before ESR1-MUT arises (presumably due to development of other resistance mechanisms). Patients who develop ESR1-MUT are at that time randomized to continuing current therapy until progression, versus changing current therapy immediately. All patients change to next-line therapy at each progression. The main end points are OS, PFS, adverse events, and patient-reported outcomes. b Possible outcomes. Selection of endpoint is important: while for the “change” arm, longer PFS might be expected, OS has multiple plausible outcomes – (H0) no change in OS, due to the same clocklike rate of resistance development; (H1) longer OS, due to the “change” arm have a higher chance of durable response with earlier therapy switch; (H2) shorter OS, due to premature discontinuation of current therapy before attaining maximum benefit