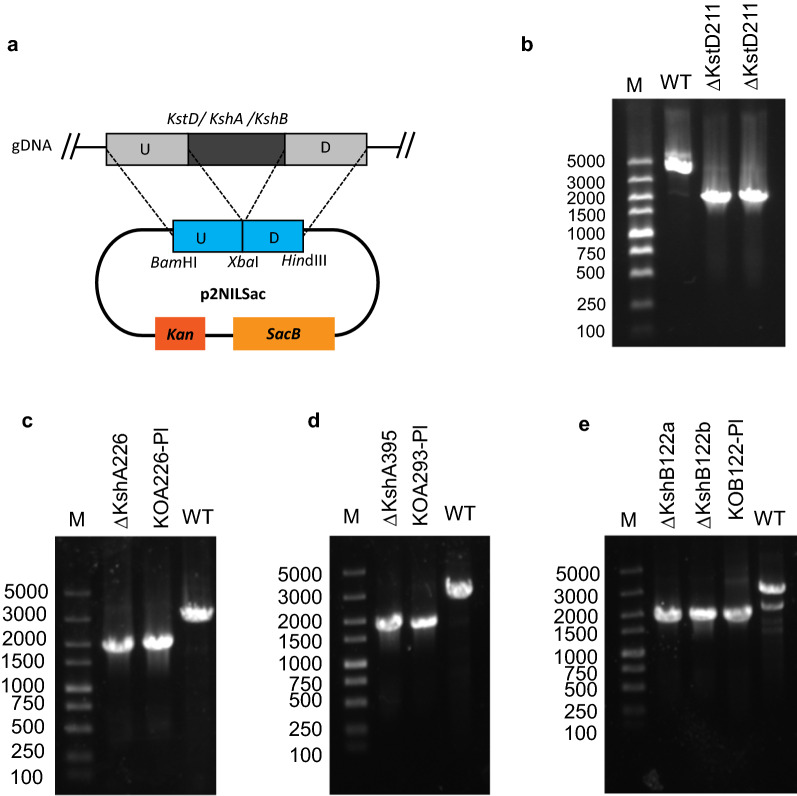
Fig. 3.
Knockout of the kstd and ksh genes from the HGMS2 strain. a A homologous recombination vector was constructed based on p2NIL plasmid. U: the upstream sequence; D: the downstream sequence. b PCR confirmation of putative kstd-knockout colonies, in comparison with that for the WT strain. M: DNA marker; WT: PCR products amplified from the HGMS2; ΔKstD211: two putative kstd-default mutants. c–e PCR confirmation of putative ksh-knockout colonies, in comparison with that for the WT strain. M: DNA marker; ΔKshA226: a putative HGMS2ΔkstD211 + ΔkshA226 mutant; KOA226-Pl: the plasmid p2NIL-Sac-ΔKshA226; WT: the HGMS2 strain; ΔKshA395: a putative HGMS2Δkstd211 + ΔkshA395 mutant; KOA395-Pl: the plasmid p2NIL-Sac-ΔKshA395; ΔKshB122a and ΔKshB122: two putative HGMS2Δkstd211 + ΔkshB122 mutants; KOB122-Pl: the plasmid p2NIL-Sac-ΔKshB122