Fig. 4.
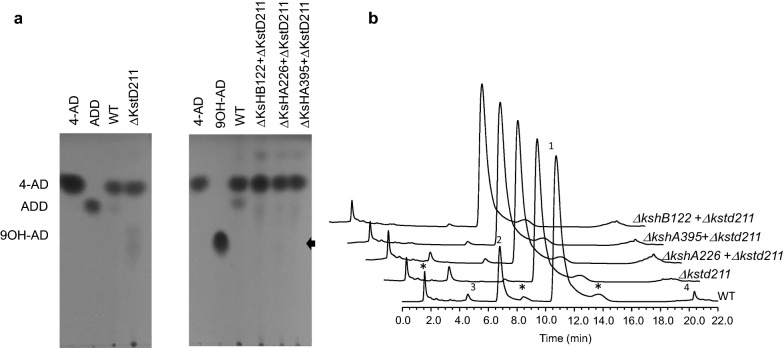
Characterization of kstd-knockout and ksh-knockout mutants for phytosterol fermentation in small-scale fermentation. a TLC assay of the catabolites by kstd-knockout and ksh-knockout mutants during phytosterol fermentation, compared with those of the WT strain and the standard samples of 4-AD, ADD and 9OH-AD. ΔKstD1, ΔKshB122, ΔKshA226 and ΔKshA395 refer to the HGMS2Δkstd211, HGMS2Δkstd211 + ΔkshB122, HGMS2Δkstd211 + ΔkshA226 and HGMS2Δkstd211 + ΔkshA395 mutants, respectively. Weak 9OH-AD spots for the samples from the HGMS2Δkstd211, and HGMS2Δkstd211 + ΔkshA226 mutants are marked by arrows. b HPLC profile of the extracts from the phytosterol fermentation by three double mutants for 144 h compared with those of the WT strain and the HGMS2Δkstd211 mutant. (1) 4-AD; (2) ADD; (3) 9OH-AD and (4) BA. Asterisk: unknown HGMS2 metabolites when the strain was cultured without phytosterol