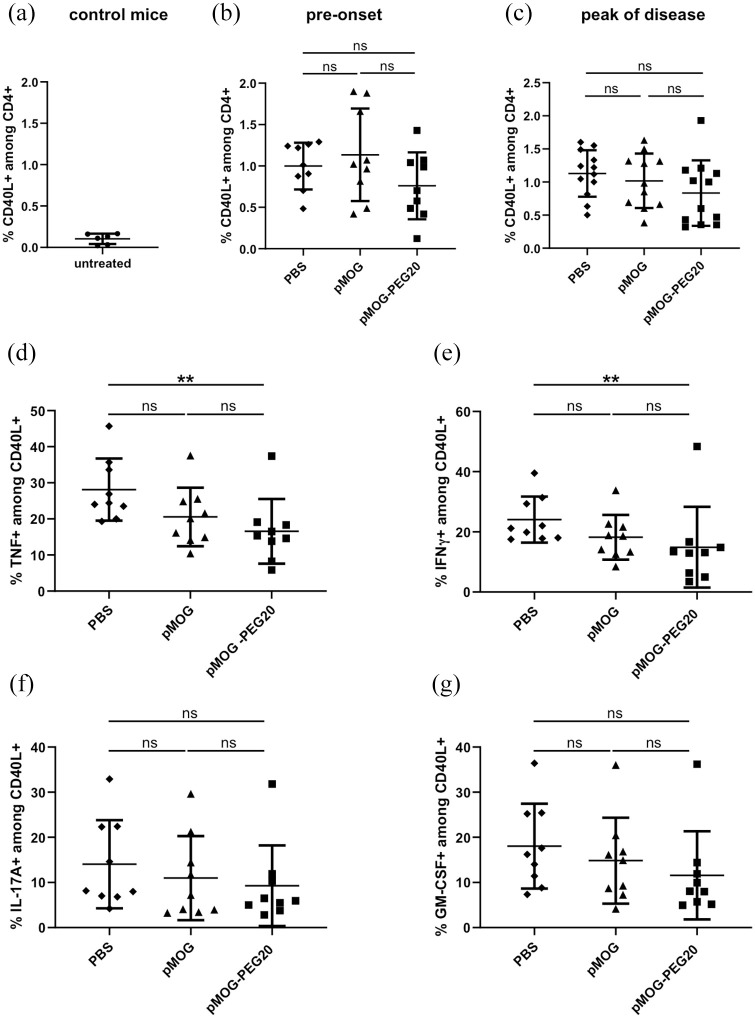
Figure 3.
In the pre-onset phase and at the peak of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the frequency of MOG-specific cells among total CD4+ splenocytes is not affected by MOG-peptide 35–55 (pMOG)-polyethylene glycol (PEG)20, while the frequency of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or interferon (IFN)-γ-producing cells among MOG-specific splenocytes is significantly decreased compared to phosphate buffered saline (PBS) by pMOG-PEG20. Seven days prior to EAE induction, C57BL/6 mice were tolerized intravenously (i.v.) with either PBS (a, control), 7.6 µg pMOG or an equimolar amount of pMOG-PEG20 (b–g). Animals were sacrificed 7 days (pre-onset phase) or 15 days post EAE induction (peak of disease). Splenocytes from single mice were re-stimulated overnight with pMOG and analyzed by flow cytometry. (a) Untreated control mice, n = 6. (b) Pre-onset phase, n = 9. (c) Peak of disease, n = 11–12 (one animal of pMOG-group had to be removed for ethical reasons). Data represent means ± standard deviation (SD) of % MOG-specific CD4+ cells (% CD40L+ on pMOG-restimulation) among total CD4+ cells. d–g: Cytokine-producers among CD4+ CD40L+ (MOG-specific) cells. Means of (d) % TNF+, (e) % IFN-γ+, (f) % interleukin (IL)-17A+ and (g) % granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)+ cells ± SD (n = 9 per group). Pooled data of two independent experiments are shown. p Values were determined by unpaired non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test.