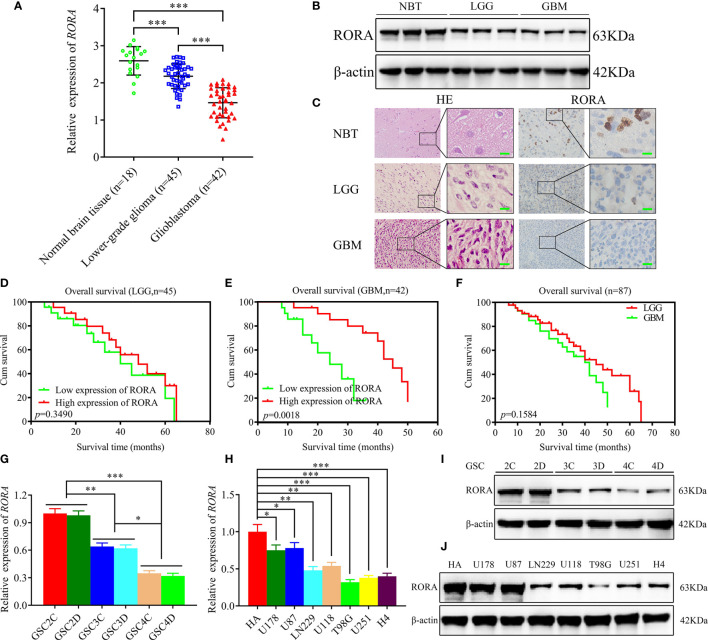
Figure 1.
Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor A (RORA) has low expression in glioblastomas and correlates with poorer patient survival, and the expression of RORA in patient-derived GSCs and GBM cell lines. (A–C) RT-qPCR (A), western blotting (B), and immunohistochemistry analyses (C) showing RORA expressions in different clinical glioma specimens, when compared with normal brain tissues (NBTs). β-actin was used as a loading control. (lower-grade glioma, LGG, n = 45; glioblastoma, GBM, n = 42; NBTs, n = 18; P < 0.001; one-way analysis of variance). Scale bar = 50 µm. (D–F) Kaplan-Meier analysis of 87 cases of glioma patients with high RORA expressions versus low RORA expressions. (G–J) RT-qPCR (G, H) and western blotting (I, J) showing RORA expression in six patient-derived GSCs and in GBM cell lines. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD (three independent experiments). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.