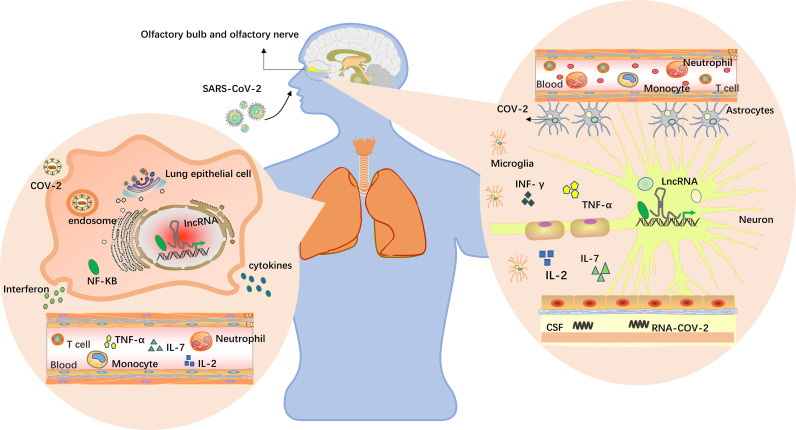
Figure 2.
LncRNAs in the brain and lungs. The virus enters the body through the nose and mouth, causing pneumonia and other symptoms. Upon oral infection, the virus reaches the lungs and, from there, can spread into the CNS by the hematogenous route. Upon nasal infection, SARS-CoV-2 can reach the CNS through the olfactory bulb (89). Viruses have been detected in the CSFs of infected patients, and inflammation in the brain has been described. Multiple studies have found that lncRNAs are differentially expressed in humans, and lncRNAs near the alveoli and olfactory bulb may be induced by viruses to participate in specific cellular activities in this region, including virus infection, replication, latent infection and immune responses. Cytokine storms occur when the immune system is overactivated, causing a surge in interleukin-2, IL-7, interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor expression (64, 90).