Figure 1.
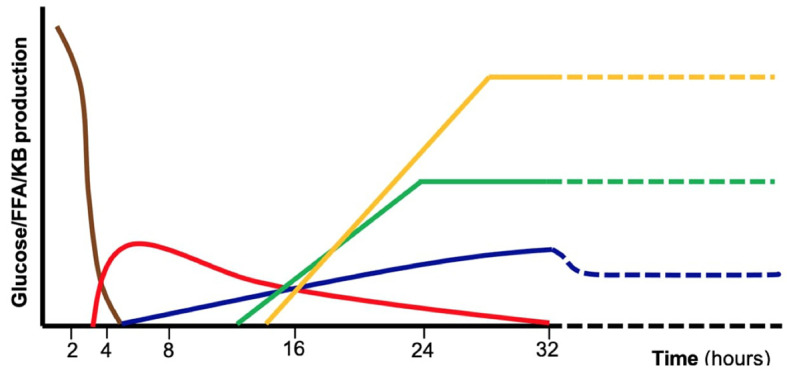
Schematic representation of the major metabolic pathways involved in glucose homeostasis during absorptive phase and fasting including exogenous carbohydrates (brown), glycogenolysis (red), gluconeogenesis (blue), fatty acid oxidation (green), ketogenesis and ketolysis (yellow). These mechanisms are tightly controlled by hormonal regulation. Defects in specific enzymes or transporters involved in those pathways as well as endocrine disorders may result in fasting intolerance and hypoglycemia. FFA, free fatty acids, KB, ketone bodies.
