Figure 3.
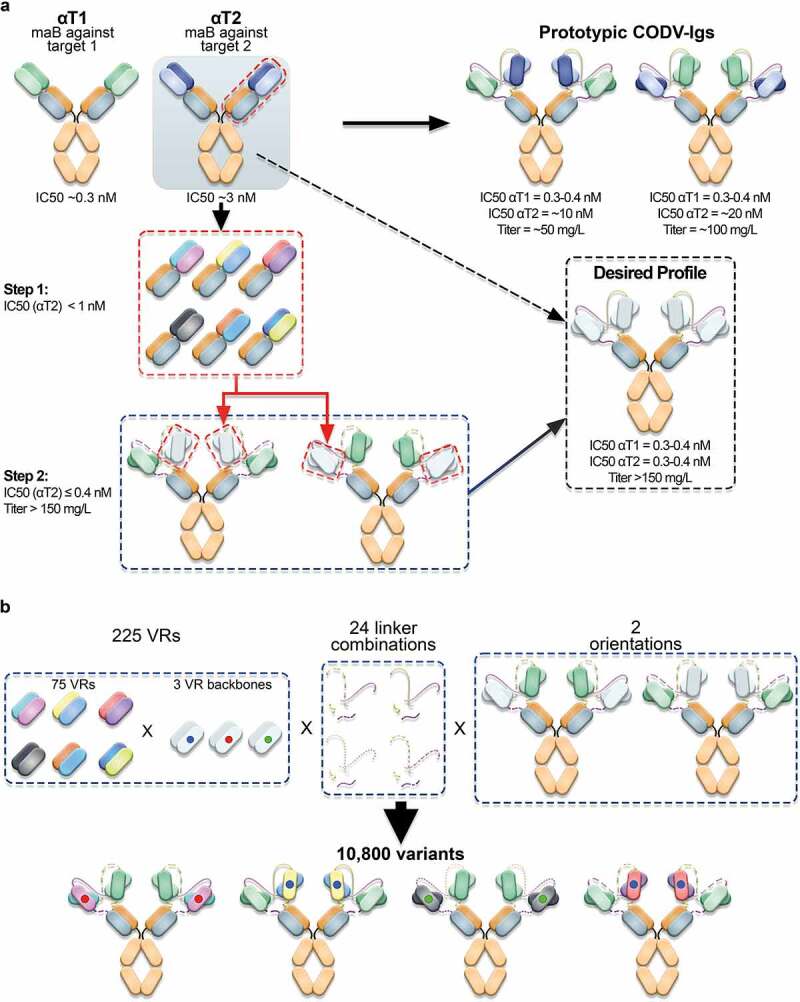
Optimization of prototypic CODV-Ig variants. a) Engineering strategy. At start, two antagonistic monoclonal antibodies (αT1 and αT2) directed against two unrelated antigens (target 1 (T1) and target 2 (T2)) were combined in a cross-over fashion in two orientations to allow for simultaneous neutralization of both targets (Prototypic CODV-Igs). The antagonistic drug potencies of the monoclonal antibodies were in the picomolar (αT1) to low nanomolar (αT2) range as determined in cell-based functional assays reflecting the inhibition of T1- and T2-mediated reporter gene activation respectively. However, when combining both antibodies in the CODV-Ig format, the inhibitory potency against T2 dropped by more than 3 fold while the IC50 against T1 remained largely unaffected. Interestingly, the bispecific αT1-αT2 CODV antibody could be produced at significantly higher titers (100 mg/L vs. 50 mg/L) when presenting the binding domain against T2 on the outer position of the CODV, which indicated additional structural constraints. Primary optimization goals were to increase potency and productivity of the prototypic CODV-Ig constructs to meet the desired profile by applying a two-step engineering approach. First the neutralization activity of the αT2 antibody should be increased to sub-nanomolar levels on the Fab level followed by accommodation of optimized αT2-VRs in the CODV-Ig format by modifying the composition of the VR connecting peptide linkers on the HCs and LCs while providing both possible VR orientations. b) Structural diversification. 75 mutational VRs designs from step1 displaying varying combinations of beneficial CDR mutations were selected to be combined with three different VR backbones in the CODV format. The VR backbones included in addition to the wildtype αT2 backbone two alternative, sequence-optimized αT2 VR backbones where potential post-translational modifications had been addressed by neutral substitutions (75 VR designs x 3 backbones = 225 VRs). The resulting 225 αT2 VR alterations were assembled with the αT1 VR in the CODV-Ig format in two orientations using 24 different peptide linker combinations, giving rise to 10,800 possible variants
